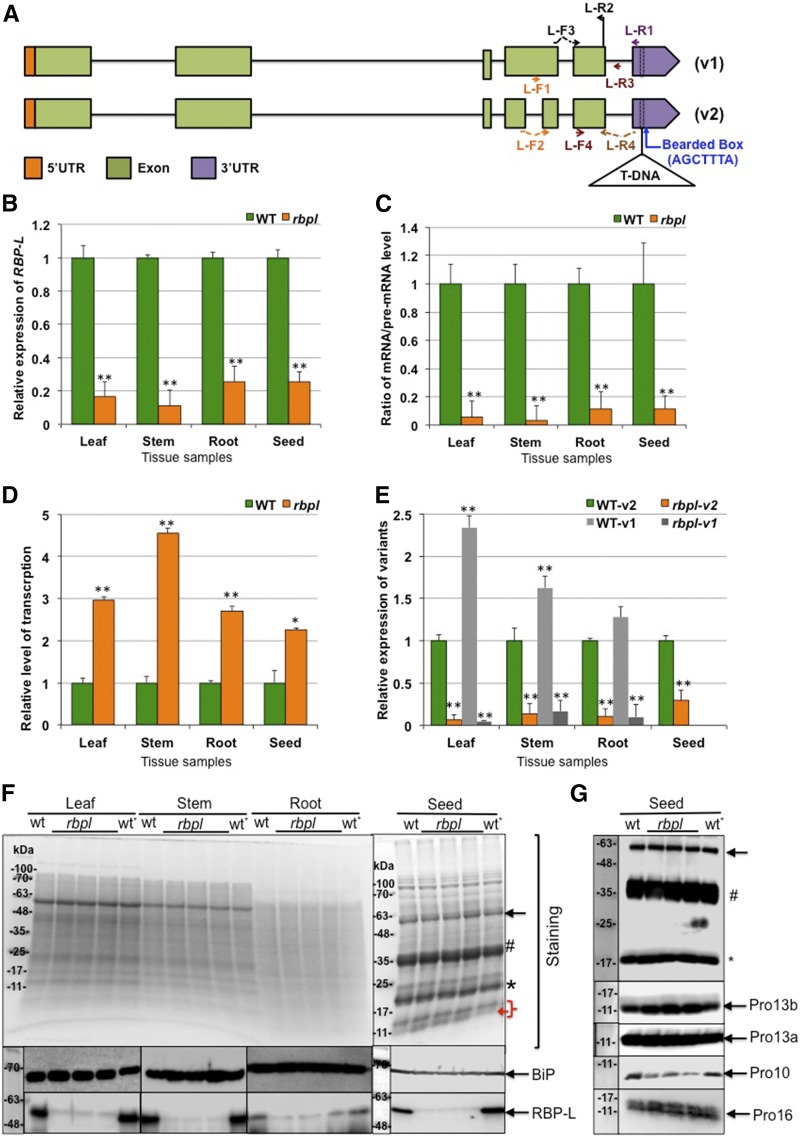
Figure 5.
Knockdown of RBP-L by a T-DNA insertion within its 3′UTR. A, Gene structure and T-DNA insertion site of the RBP-L gene. Two splicing variants are labeled as “v1” and “v2,” respectively. T-DNA insertion site is bordered by dashed lines in the 3′UTR. Arrows indicate the location and direction of the corresponding primers. B, Relative expression level of the RBP-L gene revealed by RT-qPCR using primer set of L-F3 and L-R2. C, The relative apparent splicing efficiency as denoted by the ratio of RBP-L mRNA/premRNA levels. RT of total RNA was performed using primer L-R1, and mRNA and premRNA levels amplified by primer sets of L-F3 + L-R2, and L-F4 + L-R3, respectively. D, Total transcription level of the RBP-L gene expression was determined by RBP-L gene transcripts (spliced and unspliced) amplified by primers L-F4 and L-R2. E, Relative expression of the two splicing variants of the RBP-L gene amplified by L-R4 with L-F1 or L-F2. All relative expression levels of RBP-L gene transcripts in rbpl line shown in (B) to (E) are normalized to that of wild type. **P value < 0.01. The expression level of the splicing variant v1 in developing seeds is not shown due to its low expression in developing rice grains. F, Expression level of RBP-L protein revealed by immunoblot using anti-RBP-L antibody. BiP levels as assessed by immunoblot analysis was used as a loading control. (Top) Coomassie brilliant-blue–stained SDS-PAGE; (center and bottom) the immunoblot results for BiP and RBP-L, respectively. The three lanes between “wt” and “wt*” present total protein samples from three individual plants of rbpl line. G, The differential expression of prolamine family proteins during grain development. Pro-10 polypeptides levels are depressed whereas Pro-13b polypeptides amounts are elevated in rbpl line. Black arrow, Glutelin precursor; #, acidic subunit; *, basic subunit; red bracket, prolamine polypeptide; red arrow, possible up-regulation of 13 kD prolamine polypeptides; wt, wild type; wt*, wild-type genotype segregated from heterozygous rbpl line (for detailed information, see “Materials and Methods”).