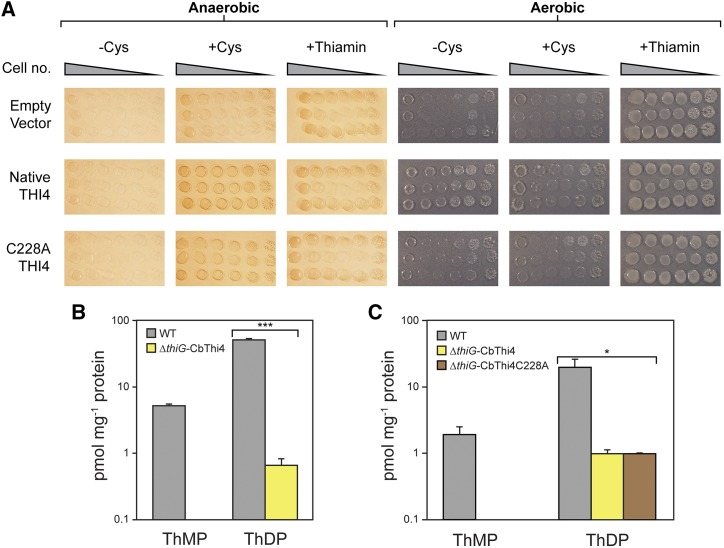
Figure 6.
Functional complementation of the E. coli ΔthiG strain by native and C228A mutant C. bicolor THI4. A, The ΔthiG strain harboring the pBAD24 vector alone or containing the native or C228A mutant form of C. bicolor THI4_1 was cultured in MOPS minimal medium containing 0.2% (w/v) glycerol and 0.02% (w/v) arabinose, plus or minus 1 mm Cys, in aerobic or anaerobic conditions. Controls supplemented with 100 nm thiamin were included. Anaerobic media contained 40 mm nitrate as the electron acceptor. Overnight liquid cultures of three independent clones for each construct were 10-fold serially diluted and spotted on the plates. Images were captured after incubation at 37°C for 7 d. B, Thiamin monophosphate (ThMP) and diphosphate (ThDP) contents (log scale) of E. coli ΔthiG cells complemented with native C. bicolor THI4_1, grown aerobically without added Cys; wild type cells grown in these conditions are included for comparison. C, Thiamin mono- and diphosphate contents (log scale) of E. coli ΔthiG cells complemented with native or C228A C. bicolor THI4_1, grown anaerobically plus 1 mm Cys; wild type cells grown in these conditions are included for comparison. Values in B and C are means and SE for three independent replicates. No thiamin monophosphate was detectable in cells complemented with native or C228A C. bicolor THI4_1. The ThDP content differences between wild type and complemented cells were significant at P < 0.0001 (***) in aerobic conditions or P < 0.05 (*) in anaerobic conditions, as determined by Student’s t test.