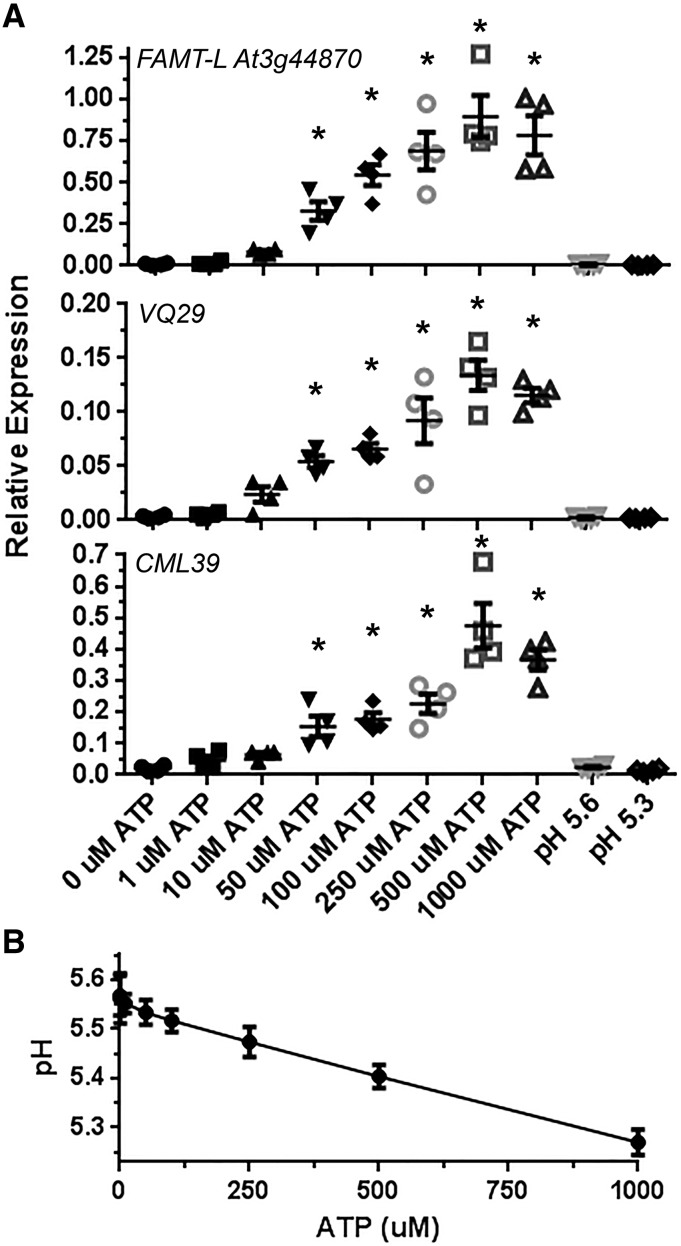
Figure 1.
Dose-dependent effect of ATP on gene expression in wild-type plants and pH in the treatment solution. A, Eight-day-old seedlings were treated with varying concentrations of ATP or with different pH levels for 30 min, and gene expression of the indicated genes was estimated by reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR; mean, individual replicate values and se are shown, n = 4). The expression of each gene was normalized by comparison with the internal control PP2A (Czechowski et al., 2005). Gene expression different from the non-ATP treatment is indicated by asterisks (P < 0.05). B, Addition of ATP to the test solution decreases the pH. Note that ATP treatment induces ATP-responsive gene expression but that pH decrease does not.