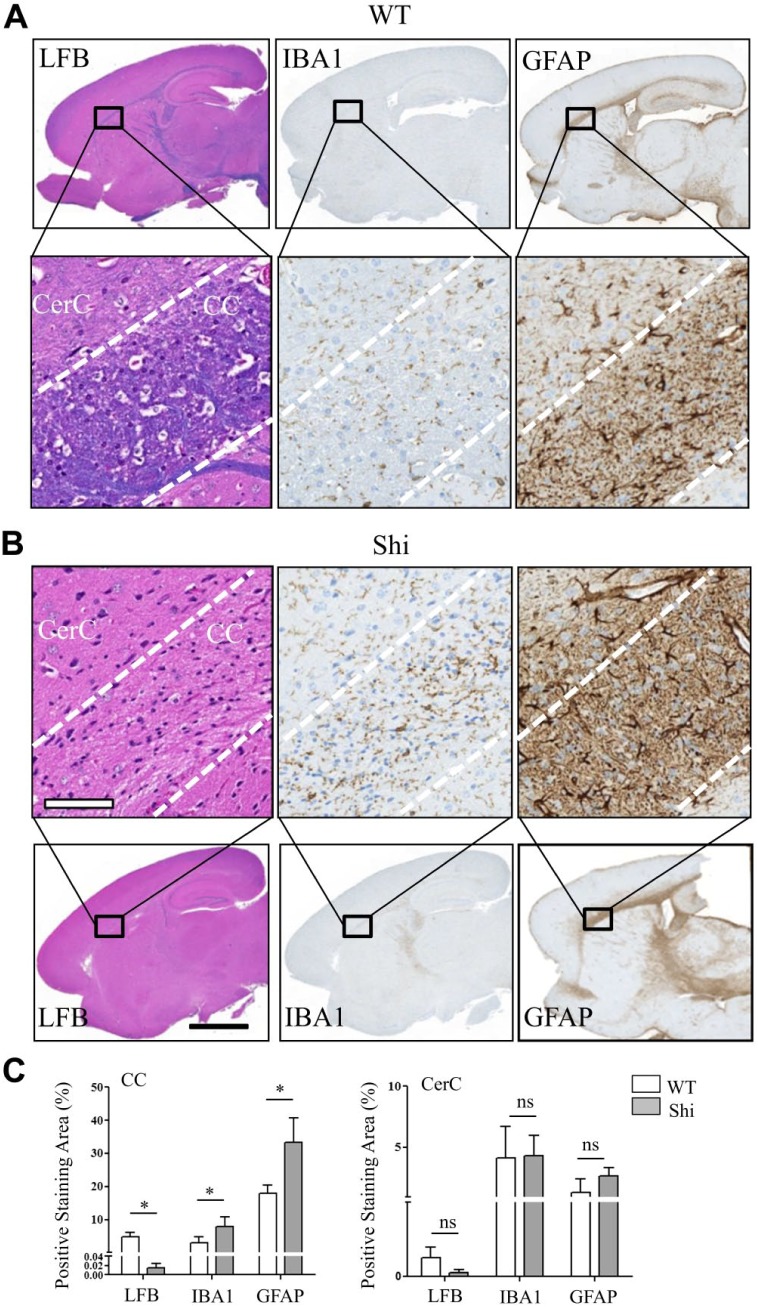
Figure 4.
Altered spatial distribution patterns of sulfatide and phosphatidylcholine species correlated with reduced myelin staining, reactive macrogliosis and reactive astrocytosis in the CC of Shi mouse brain. A full view of digital scanned images from the WT and Shi mouse sagittal brain sections stained with LFB, IBA1, and GFAP (A, top row, and B, bottom row). (A) Bottom row and (B) top row magnified views of CC and CerC of the corresponding image shown in the column. (C) Whereas the LFB positive staining was significantly decreased, the IBA1 and GFAP positive staining was significantly increased in the CC of Shi mouse. There was no significant difference between the mice of either genotype in the levels of all markers in the CerC. Unpaired two-tailed t-test; n=5; spatial resolution, 80 μm; white scale bar, 90 μm; and black scale bar, 3 mm. Abbreviations: CC, corpus callosum; Shi, shiverer; WT, wild type; LFB, luxol fast blue; IBA, ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; CerC, cerebral cortex. *p<0.05.