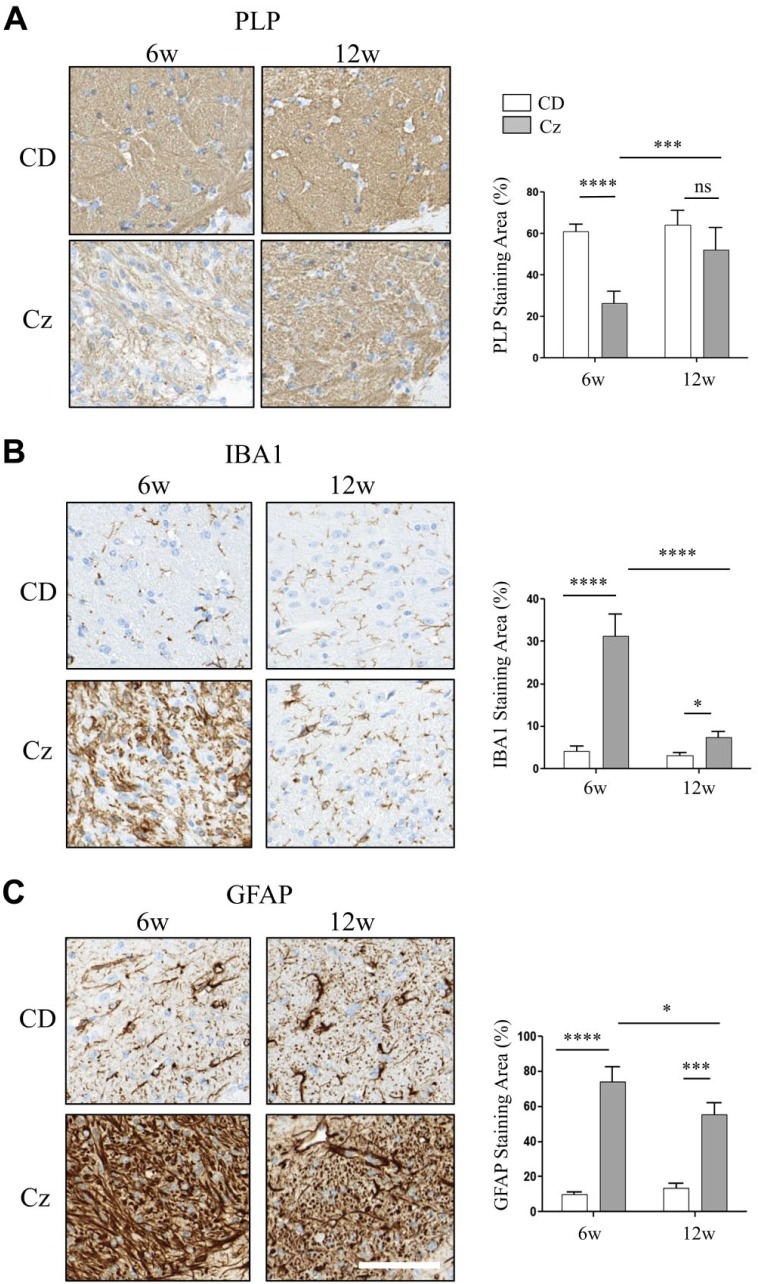
Figure 5.
Spatial and temporal distribution changes of sulfatide and phosphatidylcholine species correlated with reduced myelin staining, reactive macrogliosis, and reactive astrocytosis in the CC of Cz-fed mouse brain. (A–C) CC region of brain sections collected from the CD-fed (upper row) and Cz-fed mouse (bottom row) at 6w and 12w study time points and stained with PLP, IBA1, and GFAP, respectively. Chart next to each image show positive staining area (plotted as %). There was a significant decrease in the PLP-positive staining; whereas, IBA1 and GFAP positive staining was significantly increased in the CC of Cz-fed mouse after 6w demyelination. Consistent with remyelination, PLP staining was restored at 12w and there was no significant difference in the staining levels compared with the age-matched CD-fed mouse. By 12w, IBA and GFAP positive staining also resolved significantly compared with the 6w Cz-fed mouse. However, staining levels remain significantly elevated compared with the age-matched CD-fed mouse. Two-way ANOVA, n ranged from five to eight animals per time point, and scale bar, 90 μm. Abbreviations: CC, corpus callosum; Cz, cuprizone; CD, chow diet; PLP, proteolipid protein; IBA, ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; w, weeks. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.