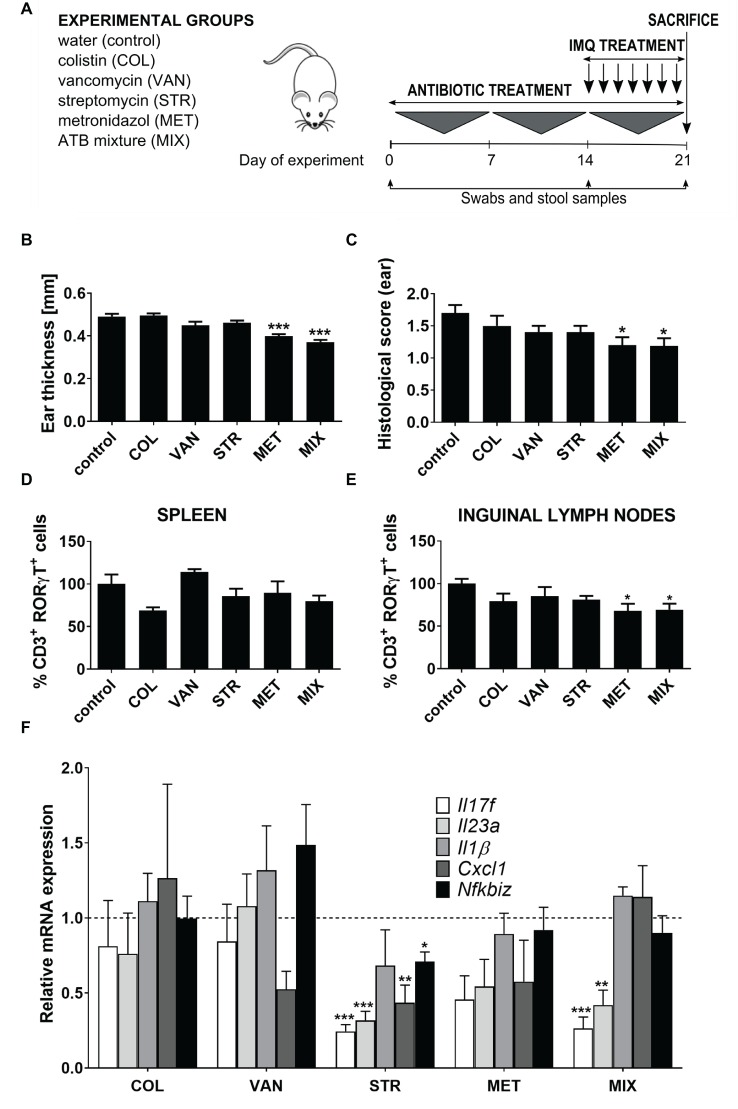
Figure 1.
Treatment with a single antibiotic or antibiotic mixture changes the susceptibility to IMQ-induced skin inflammation in BALB/c mice. (A) Experimental design: Female BALB/c mice were divided into six groups (five mice per group) and treated perorally with colistin (COL), vancomycin (VAN), streptomycin (STR), metronidazole (MET), or MIX of these antibiotics for 21 days. Starting on Day 14, mice were treated with IMQ until the end of experiment. (B,C) Quantification of ear thickness and histopathological score at the end of experiment (Day 21). (D,E) Flow cytometric analysis of expression of CD3+RORγt+ T cells in spleen and inguinal nodes. Percentage is relative to the proportion of live cells gated on CD3+ and subsequently on RORγt+ in control mice.100% represents controls gated on live CD3+RORγt+. (F) Quantitative PCR analysis of mRNA expression of Il17f, Il23a, Il1b, Cxcl1, and Nfkbiz in the skin. Data were normalized to the expression of the Elongation factor 2 (Eef2) as a reference gene. Five mice per group were analyzed, and representative data from one out of three independent experiments are shown. Statistical differences between the groups were determined by ANOVA (B–E) or by Student’s t-test (F). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.