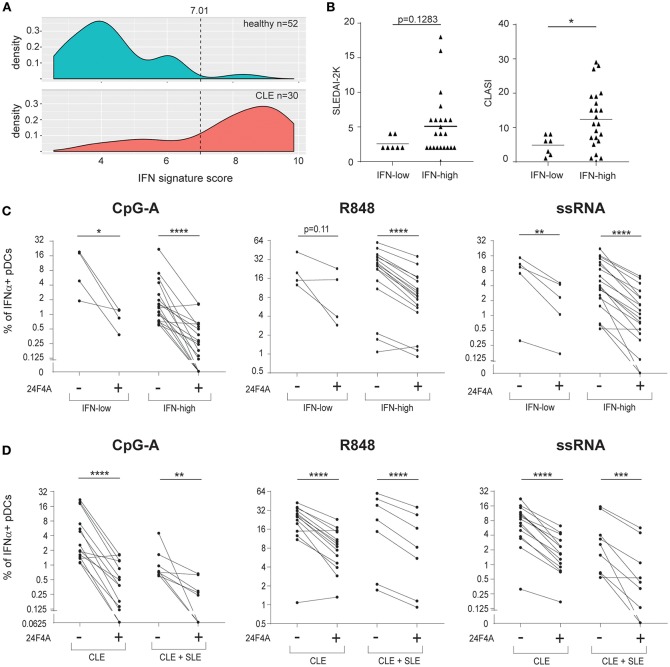
Figure 5.
24F4A further reduces pDC IFNα production after CpG-A, R848 or ssRNA stimulations of PBMC isolated from CLE patients with blood IFN-high signature or concomitant SLE diagnostic. (A) Distribution of the blood IFN signature scores in healthy individuals (n = 52) and CLE patients (n = 30). (B) Comparison of SLEDAI2-K disease scores (left) or CLASI skin scores (right) between CLE patients with blood IFN-low and blood IFN-high signature scores. Statistical significance was assessed using Mann-Whitney test (*p < 0.05). (C) Effect of 24F4A on the percentage of IFNα-producing pDCs induced by CpG-A, R848 and ssRNA stimulations and detected by flow cytometry in PBMC from CLE patients with blood IFN-low (n = 4 donors) or IFN-high signature (n ≥ 17 donors). Statistical significance was assessed with a two-tailed paired Student's t-test using log2-transformed values (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001). (D) Effect of 24F4A on the percentage of IFNα-producing pDCs induced by CpG-A, R848 and ssRNA stimulations and detected by flow cytometry in PBMC from CLE patients with or without concomitant SLE diagnostic (n ≥ 7 donors and n ≥ 14 donors, respectively). Statistical significance was assessed with a two-tailed paired Student's t-test using log2-transformed values (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001).