Fig. 6.
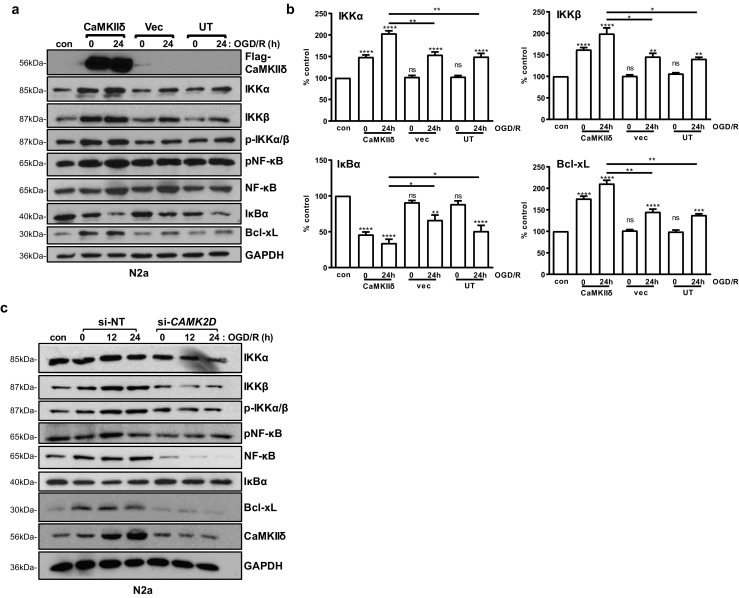
CaMKIIδ promoted neuronal survival through the NF-κB signaling pathway. a N2a cells were transfected with a Myc-DDK-CaMKIIδ plasmid. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were subjected to OGD/R for 0 and 24 h. Cells cultured in normal medium under normoxic condition were used as controls (con). The cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting as indicated. GAPDH was blotted as the loading control. Representative images from one of three independent experiments are shown. b Quantification of the levels of IKKα, IKKβ, IκBα, and Bcl-xL by densitometry analysis. Percent control (y-axis) represents the expression of the target genes to that of the controls under normoxic condition (equal to 100%). Data are the mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. ns, not significant; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 vs. control by one-way ANOVA. con, control. c N2a cells were transfected with CAMK2D siRNA (si-CAMK2D) or si-NT. After 48 h, the cells were subjected to OGD/R for 0, 12, and 24 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for members of the NF-κB signaling pathway. GAPDH was blotted as the loading control. Representative images from one of three independent experiments are shown
