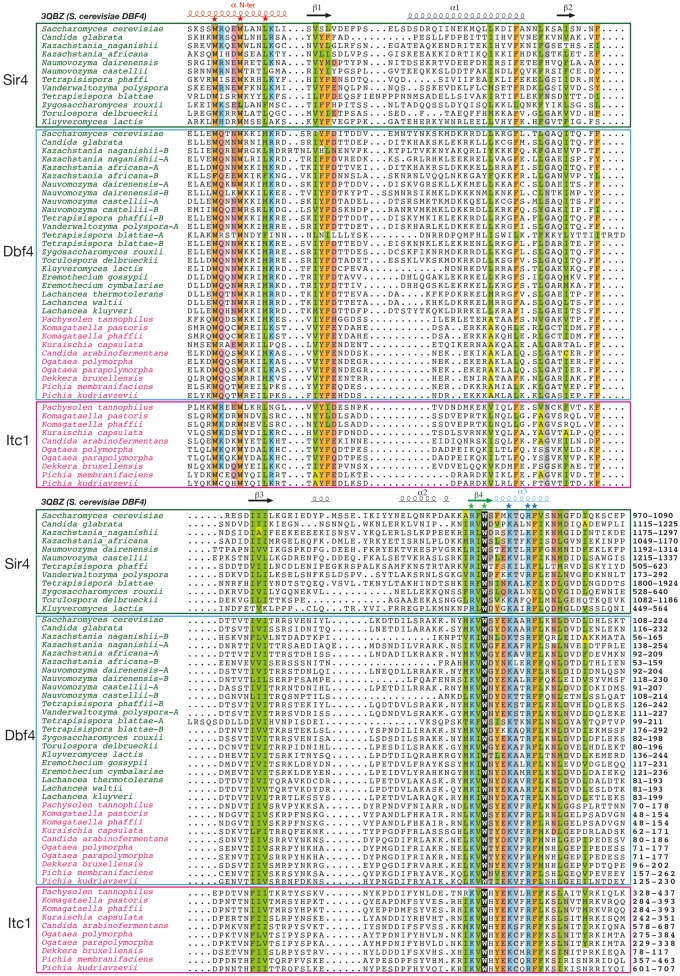
Fig. 4.
—The H-BRCT domains of S. cerevisiae Sir4 and related proteins of the Saccharomycetaceae clade and of Itc1 from the methylotrophs clade compared with those of Dbf4. Multiple alignment of the H-BRCT domain sequences. Sequences related to S. cerevisiae Sir4 belong to the group I sequences, as described in supplementary table S1, Supplementary Material online. Regular secondary structures based on the experimental 3D structure of the S. cerevisiae Dbf4 H-BRCT domain (PDB 3QBZ; Matthews et al. 2012) are reported above the alignment. Positions conserved over the entire H-BRCT family are colored in green for hydrophobic amino acids (V, I, L, F, M, Y, W), light green for amino acids that can substitute for hydrophobic amino acids in a context-dependent way (A, T, S), orange for aromatic amino acids (F, Y, W), yellow for loop-forming amino acids (P, G, D, N, S) and related amino acids (E, T), blue for basic (K, R, H) amino acids, and pink for acidic (D, E) amino acids. Highly conserved amino acids reported on the representation of the 3D structure of yeast Dbf4 H-BRCT domain (fig. 5) are depicted with stars. Domain limits are reported at the end of the sequences, and the UniProt identifiers of the sequences are reported in supplementary table S1, Supplementary Material online.