Fig. 5.
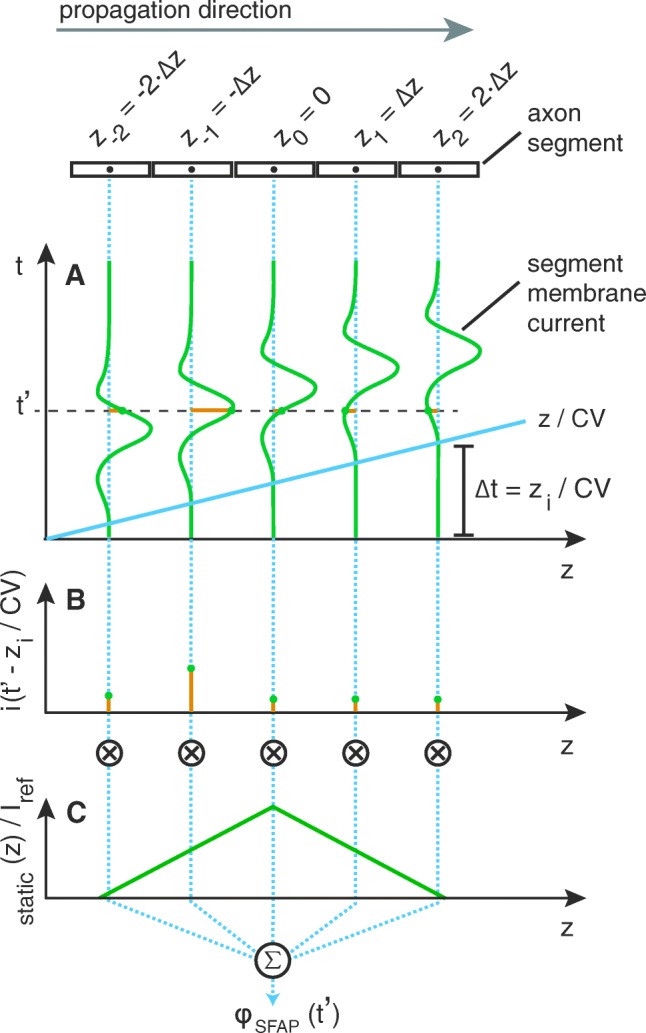
The impact of the longitudinal profile ϕSFAP(z) on SFAPs can be understood by studying the potential caused by a perfectly straight axon recorded at z0 = 0 for . Axon segments of length Δz exhibit the exact same current time course except for a delay Δt = zi/CV (a). The potential ϕSFAP at is then obtained as the sum over membrane currents shown in (b), multiplied by the static potential ϕstatic(zi,Iref)/Iref (c)
