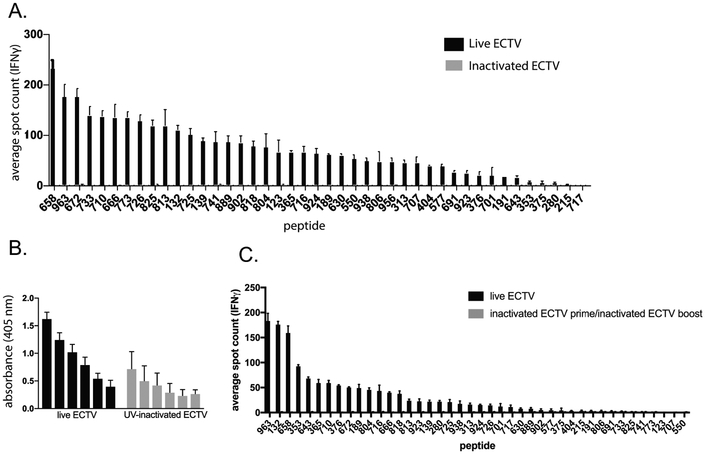
Figure 2.
Analysis of CD4+ T cell reactivity to inactivated ECTV. A. 3 Female C57Bl/6 mice were infected with either 3×103 pfu ECTV via footpad injection or 3×106 pfu UV-inactivated ECTV via i.p. injection. UV-inactivated ECTV was confirmed to be replication incompetent via plaque assay prior to injection. 10 days later mice were sacrificed. A. Spleens were pooled and CD4+ T cells were isolated by negative bead selection and mixed with peptide pulsed BMDCs and analyzed for IFNγ production by ELISpot. Representative of 3 independent experiments. B. Serum was analyzed for levels of virus-specific IgG antibodies by ELISA and background subtracted from pooled naïve serum. C. 3 Female C57Bl/6 mice were immunized with either PBS or 3×106pfu UV-inactivated ECTV via i.p. injection. 28 days later the mice were infected with either 3×103 pfu ECTV via footpad injection (live prime group) or 3×106pfu UV-inactivated ECTV via i.p. injection (inactivated ECTV prime/boost group) respectively. 10 days later spleens were pooled and CD4+ T cells were isolated by negative bead selection and mixed with peptide pulsed BMDCs and analyzed for IFNγ production by ELISpot. Representative of 3 independent experiments.