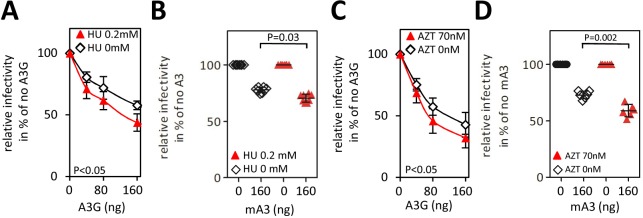
Fig 5. Reduction of intracellular dNTP concentrations and the presence of an RT inhibitor sensitize MMTV to A3s.
(A and B) Intracellular dNTP concentrations affect the sensitivity of MMTV to A3s. Target cells were treated (4 h before infection) with a drug inhibiting ribonucleotide reductase, hydroxyurea (HU), before they were challenged with virus stocks prepared in cells expressing increasing amounts of A3G (40, 80 and 160 ng) and mA3 (160 ng), respectively. The HU treatment continued for an additional 20 h. A two-way ANOVA was used to analyze data obtained with A3G from three independent infection experiments. An unpaired two-tailed t-test was used to analyze data with mA3 obtained from six infection replicates. (C and D) Sub-optimal concentrations of an RT inhibitor, AZT, sensitize MMTV to inhibition with A3G or mA3. The IC50 concentration of AZT (70 nM), was added to target cells together with the virus inoculum. The virus was removed three hours after infection and a culture medium supplemented with AZT (70 nM) was added to the cells. A two-way ANOVA (C) or unpaired two-tailed t-test (D) was used to analyze data from three (C) or six (D) independent infection experiments. (A–D) Detection of GFP+ cells was performed as described for Fig 1D.