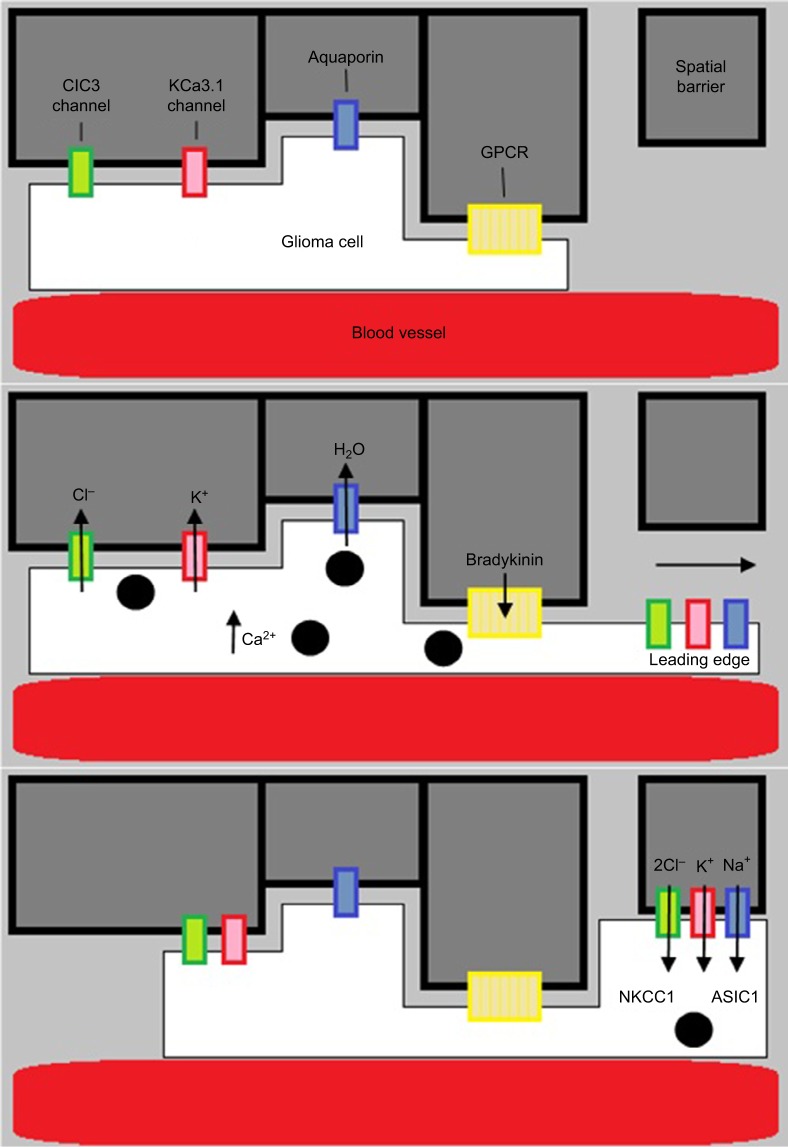
Figure 3.
Diagram showing the hydrodynamic model of invasion.
Notes: Activation of GPCR (eg, by bradykinin binding to B2R) causes intracellular Ca2+ to rise, leading to Ca2+-dependent K+ and Cl− efflux through CIC3 and KCa3.1 channels. Water then follows out of the cell through aquaporins down its osmotic gradient. This decreases cellular volume, allowing the glioma cells to migrate. They then increase volume via ion influx through NKCC1 and ASIC1 channels.