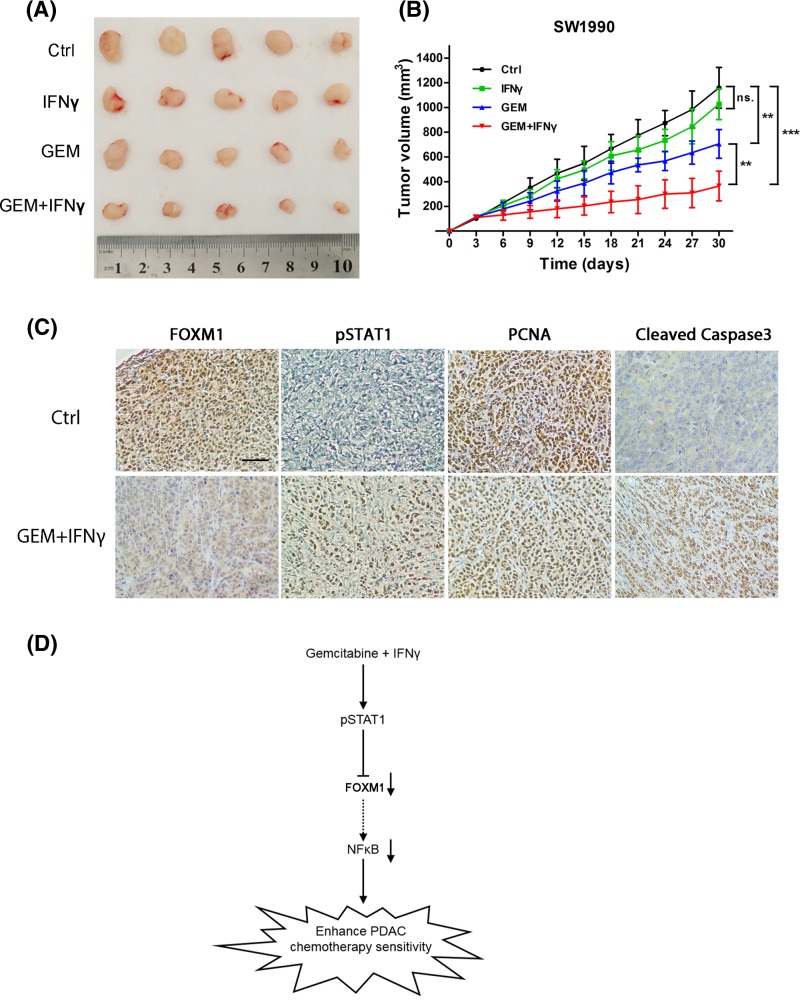
Figure 8. IFNγ inhibits FOXM1 sensitization to gemcitabine in pancreatic xenograft tumors.
(A,B) SW1990 cells were subcutaneously injected into the left flank of nude mice. Administration of chemotherapy began when the tumor diameter reached 3–5 mm. The mice were randomly divided into four groups (n=5) and treated as described in figure. (A) Tumor size was measured after approximately 30 days of treatment. (B) Tumor volumes were measured every 3 days. A tumor growth curve was drawn according the measured tumor volume. (C) The representative tumor tissue sections from xenografts in different treatment groups, analyzed by IHC for the expression of FOXM1, pSTAT1, the proliferation markers PCNA and apoptotic marker Cleaved Caspase3. Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) A schematic model showing the potential roles of IFNγ in enhancing the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine. IFNγ suppresses the expression of FOXM1 by activating STAT1, causing inhibition of NFκB signaling, which results in increased sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.