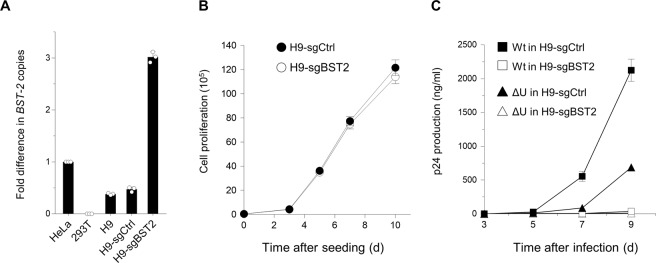
Figure 4.
CRISPR-mediated enhancement of BST-2 expression leads to marked decrease in wild-type HIV-1 replication. (A) CD4-positive H9 cells with an intermediate level of BST-2 expression were transduced with lentiviral CRISPR activation vector expressing an empty sgRNA (H9-sgCtrl) or an sgRNA targeting BST-2 promoter (H9-sgBST2), the latter of which were cloned. Cells were analyzed by real-time RT-PCR for BST-2 expression. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown as a fold difference in BST-2 copies compared with those in HeLa cells (mean ± s.d., n = 3 technical replicates). (B) Cell proliferation of CRISPR-transduced H9 cells (H9-sgCtrl, closed circles; H9-sgBST2, open circles). The assay was started with 20,000 cells. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Virus replication in H9-sgCtrl (closed symbols) or H9-sgBST2 (open symbols). Cells (1 × 105) were infected with 0.1 ng of p24 antigen of either wild-type (squares) or Vpu-defective (triangles) NL4-3 viruses. Supernatants were harvested at two-to-three-day intervals, and virus replication was monitored by p24 ELISA. Data shown are representative of four independent experiments.