Figure 5.
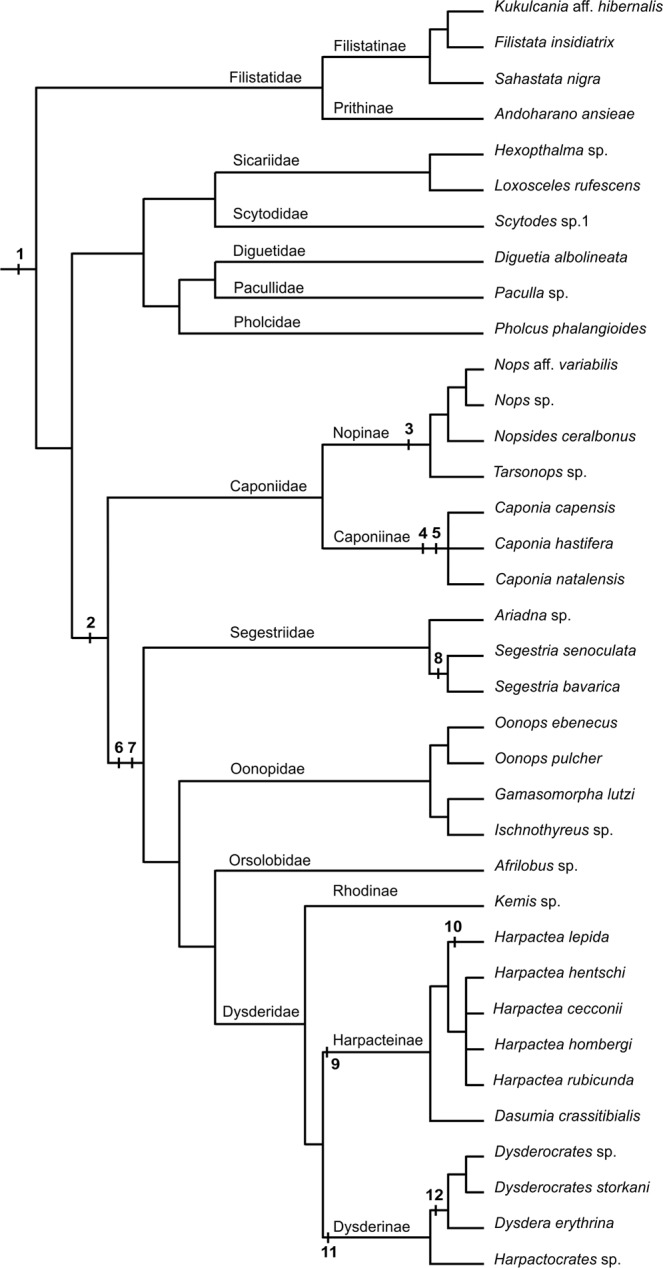
Hypotheses on haplogyne chromosome evolution. Suggested events (numbers in bold): 1 (2n♂~40, X1X2Y; ancestral karyotype of haplogynes), 2 (duplication of genome in common ancestor of Caponiidae and Dysderoidea; the latter includes Segestriidae, Oonopidae, Orsolobidae, and Dysderidae), 3 (X1X2X3X4Y1Y2, ancestral sex chromosome system of Nopinae), 4 (duplication of genome in Caponia ancestor), 5 (X1X2X3X4X5X6Y1Y2, ancestral sex chromosome system of Caponia), 6 (origin of holokinetic chromosomes), 7 (2n♂ = 7, X0, ancestral karyotype of Dysderoidea), 8 (concerted fission of all chromosomes in ancestor of Segestria), 9 (origin of inverted meiosis of sex chromosome in ancestor of Harpacteinae), 10 (2n♂ = 25, 2n of Harpactea lepida), 11 (2n♂ = 9, ancestral 2n of Dysderinae), 12 (prominent X chromosome, synapomorphy of Dysdera and Dysderocrates). Tree topology is based on Wheeler et al.19, except for filistatids (resolved according to Gray54), nopines (based on Sánchez-Ruiz & Brescovit55), and Harpactea (based on cytogenetic data of this study).
