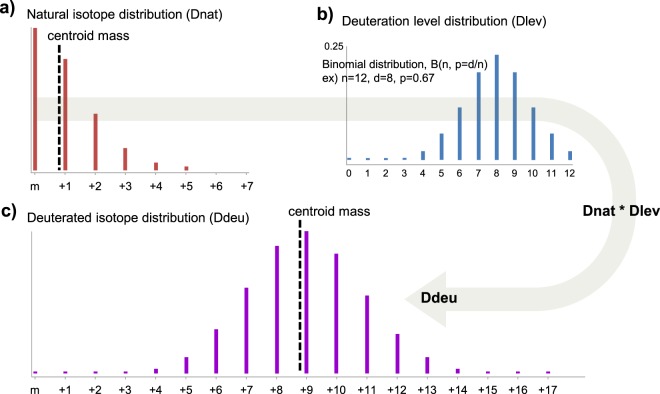
Figure 3.
Three distributions in HDX-MS data. In this example, among 12 exchangeable hydrogens of a peptide, 8 are deuterated on average. A peptide is deuterated following binomial behavior, where each of n exchangeable hydrogens in a peptide is statistically deuterated with identical labeling probability p, which is calculated by dividing the average deuterium number d by n. As a result, observed, deuterated isotopic distribution is represented as the convolution of natural isotopic distribution and statistical deuteration distribution. The dotted line represents the centroid mass (CM) of the distribution. The centroid mass-based methods calculate the average deuterium number as CM(Ddeu) minus CM(Dnat).