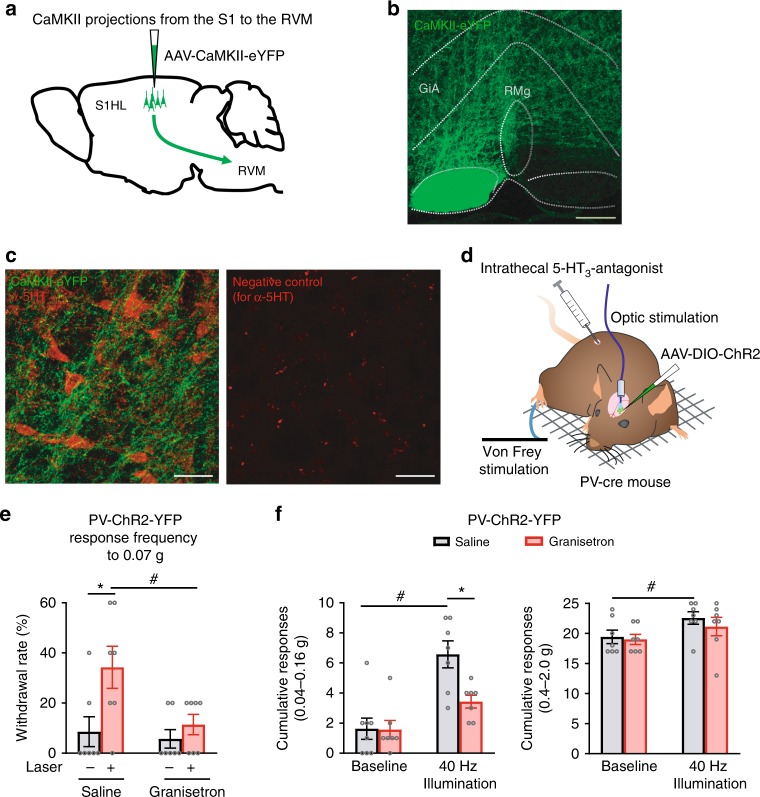
Fig. 9.
Traced projections from the S1HL to important pain modulatory centers in the rostroventral medulla (RVM) and functional contribution of descending serotonergic pathways to nociception by gamma activity in the S1. a Schematic representation of the viral tracing experiments. b Example image of viral tracing of projections from pyramidal neurons expressing eYFP (in green) in the S1HL to the RVM (observed in the raphe magnus nucleus (RMg) and the gigantocellular reticular nucleus, alpha (GiA)). c Immunohistochemical identification of serotonergic neurons (in red) in the proximity of afferent projections from the S1HL to the RMg. The right panel depicts an example of a negative control image for anti-5HT staining. d Scheme of the experimental procedure for e and f is shown. e Suppression of hypersensitivity induced by optogenetically enhancing gamma activity in the S1HL upon intrathecal injection of the serotonin receptor antagonist, granisetron (n = 7), but not vehicle (saline, n = 8). f The cumulative responses to lower (left panel) and higher intensities (right panel) of von Frey forces applied to the paw. #p < 0.05 compared to respective baseline, *p < 0.05 compared between groups, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparisons. Scale bars represent 200 µm and 50 µm in b and c, respectively. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.M.