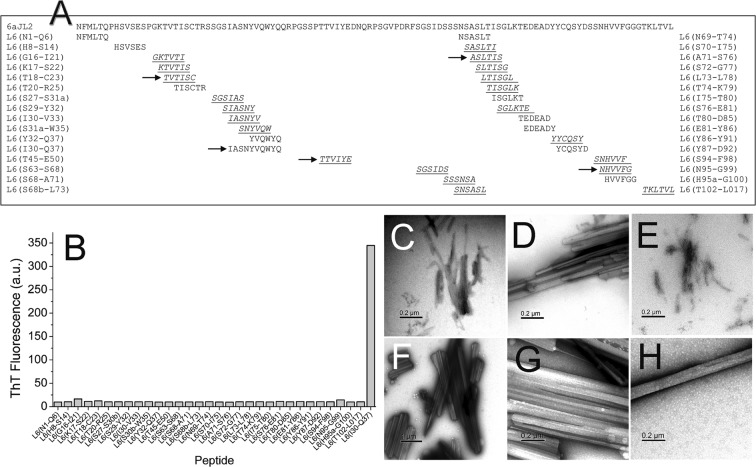
Figure 3.
(A) Prediction-based synthetic peptide library composed of thirty-one hexapeptide and one decapeptide designed for testing the predictions of fibrillogenic/aggregation prone sequences in the rVL protein 6aJL229 generated by the web-based computational tools ZipperDB26 and AmylPred228. The arrows point the consensus sequences predicted to be aggregation/fibrillogenic-prone by the tool AmylPred2. The sequences underlined and italized represent the hexapeptides forming steric zippers with a fit energy of −23 kcal/mol or lower, as calculated with RosettaDesign71. Segments with energies equal to or below this threshold are deemed to have high fibrillation propensity27. (B) Aggregation assay of the synthetic peptides composing the prediction-based peptide library. The data represented is the thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence intensity of the peptide samples (250 µM peptide dilution in PBS pH 7.4 plus 0.05% Na Azide), measured after 24 hours of incubation at 37 °C with constant agitation. Two replicas of the experiment were performed with very similar results (Result not shown). (C–H) Transmission electron micrographs of the aggregates present in the end-point samples of the synthetic peptides Ile30-Gln37 (C,D), Ile30-Val33 (E), and Ser30b-Trp35 (F–H).