Fig. 1.
Long noncoding RNA function.
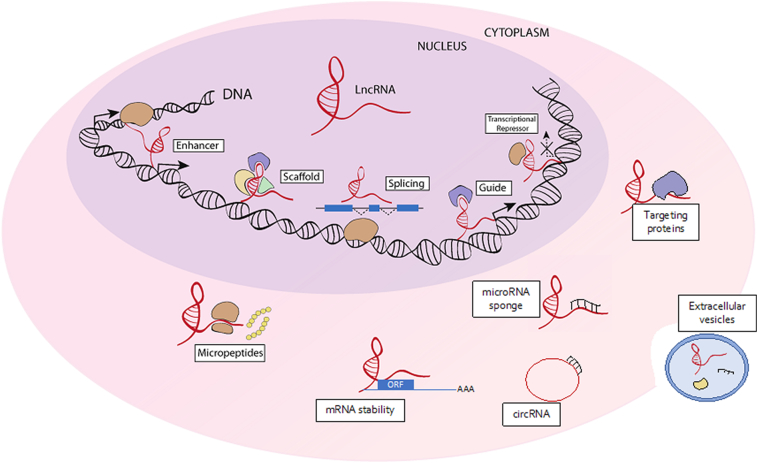
In the nucleus, lncRNAs can modulate gene expression by enhancing or repressing the transcription of specific genomic loci by recruiting chromatin modifying complexes or inhibiting the binding of transcriptional factors to their DNA targets [39]. They can also modulate the splicing process by inducing or inhibiting the abundance of specific transcripts [14]. In the cytoplasm they can modulate gene expression at post-transcriptional level, interacting with proteins or other ncRNAs (microRNAs and mRNAs). Many lncRNA seem to act as scaffold for the assembling of proteins involved in same molecular networks [40]. Some of them can also regulate the processing of their mRNA including translation and degradation [41]. LncRNA can act as molecular sponges for microRNAs thus limiting their capability to bind their targets. LncRNA can also encode short functional peptides called (micropeptides) [42]. Recentely, lncRNA have also been described as important players of cell-cell communication being secreted in the extracellular environment by extracellular vesicles [43].