Figure EV3. Conformational rearrangements in the disome.
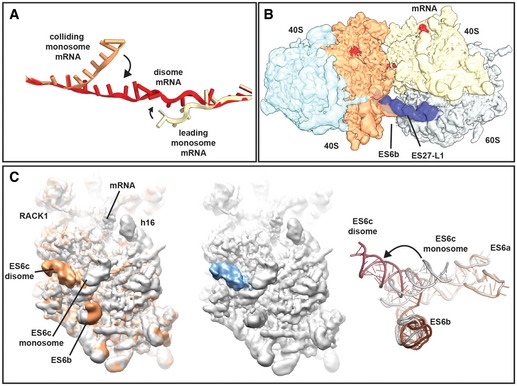
- mRNA was modelled into the refined maps of the hybrid A/P‐P/E tRNA containing monosome and the P/P tRNA containing monosome with ES27 in the L1 conformation (see Appendix Figs S4 and S6). These ribosomes are not involved in disome formation and show density for mRNA in covering approximately 30 nucleotides in the canonical path. In the disome, the mRNA deviates from the canonical path at the exit site of 5′ mRNA and at the entry site of the 3′‐mRNA in the colliding ribosome. In the disome, the corresponding nucleotides are stretching out to connect leading and colliding ribosome.
- Superposition of the disome map shown as in Fig 4A with the isolated ES27 density from the refine monosome sub‐class representing the P/P tRNA containing ribosome with ES27 in the L1 position (blue). Note that ES27 would clash with the 60S‐40S disome bridge involving ES6b.
- Left panel: superposition of the refined colliding ribosome from the disome (yellow orange) with the hybrid A/P‐P/E tRNA containing monosome (grey; see Appendix Figs S4 and S6). The view focuses on ES6. Middle panel: superposition of hybrid A/P‐P/E tRNA containing monosome with the difference map. Note that the only significant difference is in ES6c. Right panel: superposition of molecular models for ES6 in a disome (dark red/brown) and in a monosome (grey).
