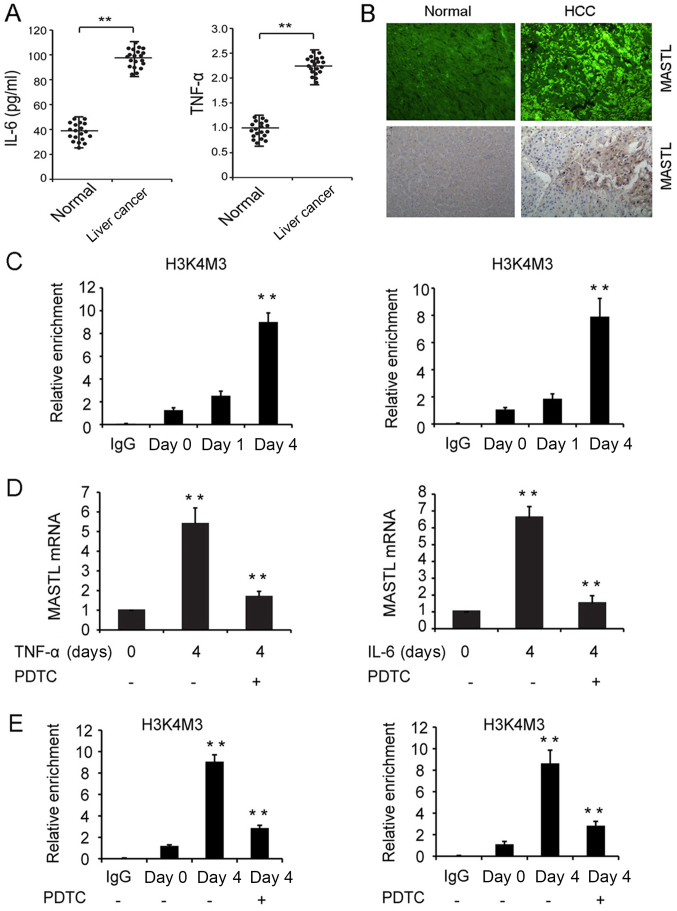
Figure 4.
Expression of MASTL in human liver samples and the mechanisms involved in the IL-6 and TNF-α-induced expression of MASTL in liver cancer cell lines. (A) IL-6 and TNF-α quantification in healthy and liver cancer patient sera by ELISA. (B) Detection of MASTL in liver cancer and non-tumor liver tissues by immunofluorescence or immunohistochemistry (magnification, ×50). (C) ChIP assay of H3K4Me3 modification at the MASTL promoter in HepG2 cells treated with IL-6 (right) and TNF-α (left) at indicated time points. (D) MASTL mRNA expression in HepG2 cells pretreated with or without PDTC (30 µmol/l) in response to IL-6 and TNF-α stimulation. (E) ChIP assay of H3K4Me3 modification pretreated with or without PDTC at indicated time points. Experiments were repeated three times. Results are displayed as the mean ± standard error of the mean. **P<0.01 vs. respective controls. MASTL, microtubule associated serine/threonine kinase-like; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6, interleukin 6; PDTC, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; IgG, immunoglobulin G.