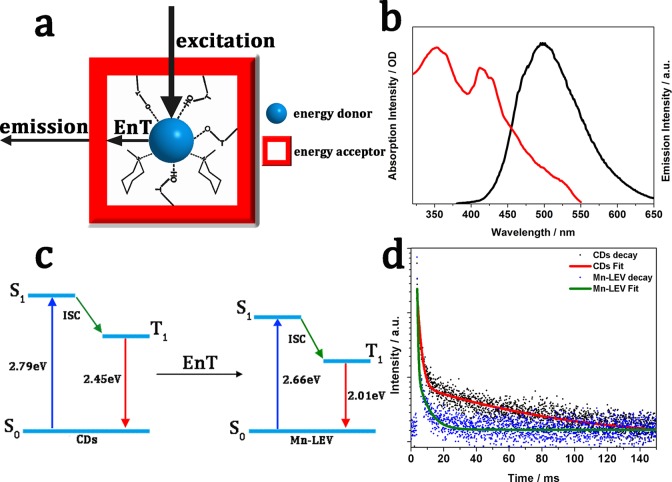
Figure 4.
Proposed mechanism for CDs@Mn-LEV composites and the EnT process between CDs and the zeolite matrix. (a) Schematic of CDs confined in Mn-LEV zeolite. The CDs are well-stabilized by hydrogen bonds of the framework and templates. Meanwhile CDs and Mn-LEV zeolite serve as the energy donor and acceptor in the EnT process, respectively. (b) UV–vis absorption spectrum (red) of the Mn-LEV framework and emission spectrum (black) of CDs. (c) Energy diagram of CDs and Mn-LEV. The triplet energy (T1) is determined by the phosphorescence emission maximum (505 and 616 nm for CDs and CDs@Mn-LEV, respectively). The singlet energy (S1) is determined by the fluorescence emission maximum (444 and 460 nm for CDs and CDs@Mn-LEV, respectively). ISC: intersystem crossing. EnT: energy transfer. (d) Lifetime decays of the CDs (black, 77 K) and CDs@Mn-LEV (red, 77 K) at 500 nm. The spectra were recorded upon excitation at 360 nm.