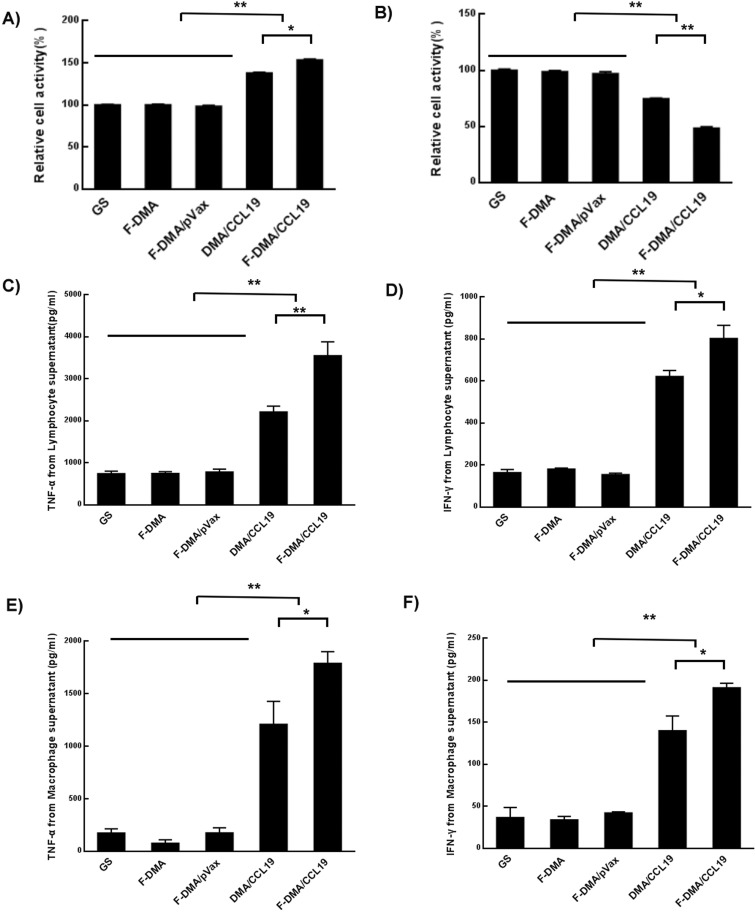
Figure 8.
F-DMA/CCL19 stimulated the cytotoxicity of T lymphocytes. When CT26 cells were transfected with GS, F-DMA, F-DMA/pVax, DMA-CCL19, and F-DMA/CCL19 for 72 h, the supernatants from different treatments were added into lymphocytes and treated for 24 h, and the lymphocyte activity was tested by the MTT test (A). When the lymphocytes were treated for 24 h, the supernatants were added to CT26 cells and treated for 24 h, and the CT26 cell activity was tested by MTT (B). The lymphocytes were treated for 24 h with cell culture supernatants collected from GS. F-DMA, F-DMA/pVax, DMA/CCL19, and F-DMA/CCL19 groups, and the corresponding supernatants after 24 h of culture in each group were then collected for measurement of IFN-γ (C) and TNF-α (D) level. The lymphocytes were treated for 24 h with cell culture supernatants collected from GS, F-DMA, F-DMA/pVax, DMA/CCL19, and F-DMA/CCL19 groups, and the corresponding supernatants were then applied to culture macrophages, and then the culture medium was collected for measurement of IFN-γ (E) and TNF-α (F). F-DMA/CCL19 mediated IFN-γ and TNF-α expression was substantially higher than that of other groups. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 when compared with GS, F-DMA, or F-DMA/pVax-treated groups. The results represent three independent experiments.