Figure 4.
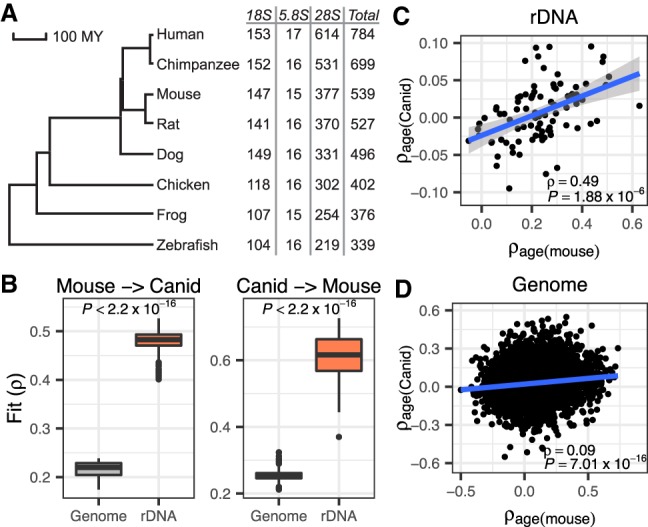
The ribosomal rDNAm clock is conserved between distantly related taxa. (A) Phylogenetic tree of seven vertebrate species with the number of homologous CpGs in each species (relative to human). (B) Interspecific mouse-canid clock models built using homologous CpGs in the rDNA yielded significantly better performance than those built using homologous genome-wide CpGs. Here, the model is trained in one species and applied to the other species. The fit is measured as the correlation coefficient (ρ) between rDNAm age and chronological age in the testing species. (C) Homologous CpGs from the rDNA show conserved age association (ρage) between mice and canids (ρ = 0.49, P = 1.88 × 10−6). (D) Homologous CpGs elsewhere in the genome show age association that is weakly correlated between mice and canid (ρ = 0.09, P = 7.01 × 10−16).
