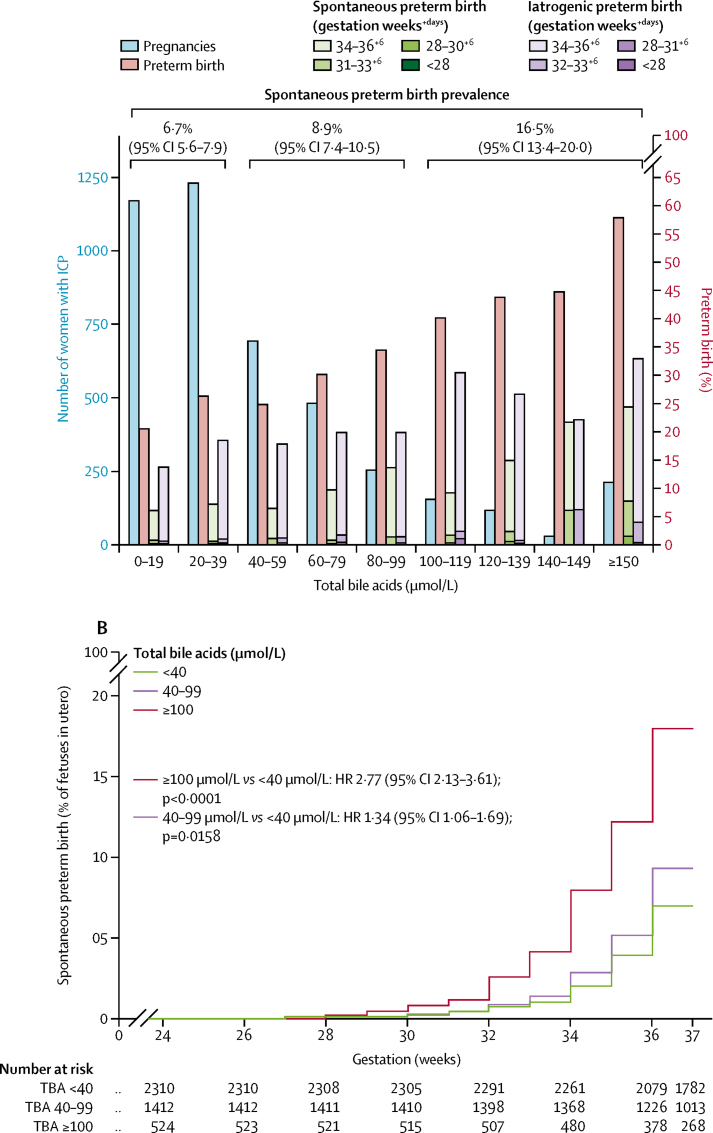
Figure 5.
Proportion of preterm births, number of pregnancies, and time-to-event analysis, by total bile acid concentrations in singleton pregnancies with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
(A) Number of women with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (blue bars), and proportion of those women with overall preterm birth (red bars), spontaneous preterm birth by gestational week (green bars), and iatrogenic preterm birth by gestational week (purple bars), by peak total bile acid category for women with singleton pregnancies. Spontaneous preterm birth (more clinically relevant than overall preterm birth because it is not clinician dependent) prevalence by total bile acid groups (<40 μmol/L, 40–99 μmol/L, and ≥100 μmol/L or more) is shown at the top of the graph. (B) Kaplan-Meir plot showing the proportion of fetuses in utero who underwent spontaneous preterm birth from 24 to 37 gestational weeks for singleton pregnancies (birth from 37 gestational weeks is not considered preterm). Data were analysed by completed gestational week categories, with alterations plotted mid-week to reflect uncertainty by individual day of change. HR=hazard ratio. ICP=intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.