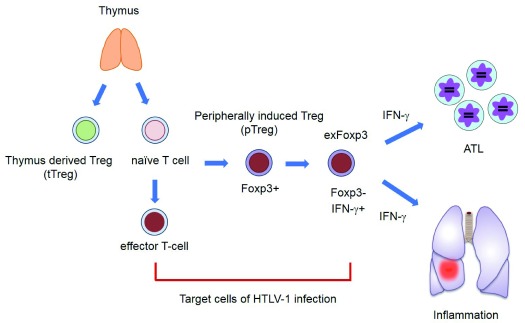
Figure 2. Inflammatory phenotype of HTLV-1–infected cells triggered by HBZ.
Target cells of HTLV-1 are effector/memory T cells and Foxp3 + T cells in vivo. HBZ promotes the transcription of the Foxp3 gene by enhancing transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)/Smad signaling, which leads to the peripheral increase of induced Tregs (iTregs) and Foxp3 + T cells. However, note that Foxp3 expression is unstable in these cells. When Foxp3 expression is lost, “exFoxp3” cells produce IFNγ, which causes inflammation and promotes leukemogenesis. HBZ, human T-cell leukemia virus-1 bZIP factor; HTLV-1, human T-cell leukemia virus-1; IFNγ, interferon gamma; Treg, regulatory T.