Fig 1. Standardized cumulative all-cause mortality by type of facility among institutionalized residents in Madrid, Spain.
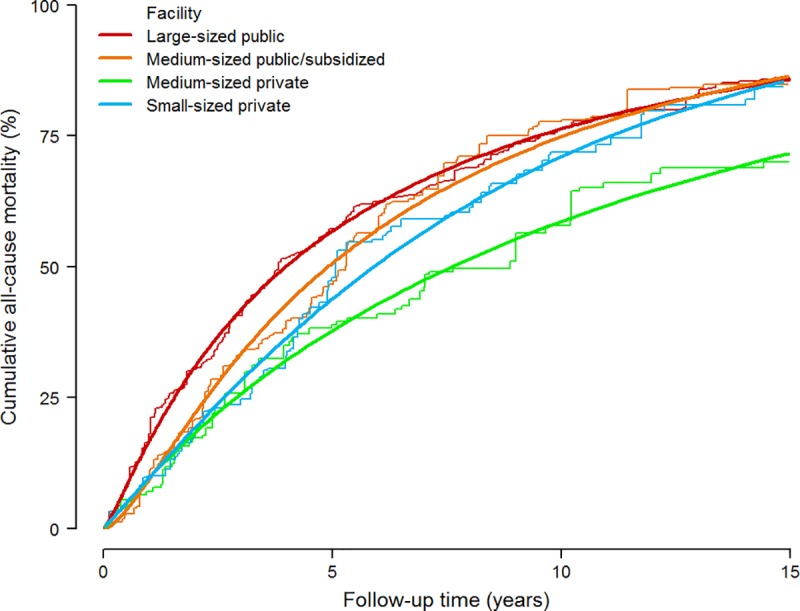
Parametric cumulative mortality curves (smooth lines) were estimated from a spline-based survival model and nonparametric cumulative mortality curves (step functions) from Kaplan-Meier methods, both weighted by combined inverse probability weights and stratified by type of facility. Combined weights were used to standardize cumulative mortality curves in each type of facility to the weighted distribution of baseline confounders in the overall institutionalized population, including age (65–74, 75–79, 80–84, 85–89, or ≥90 years), sex (female or male), educational level (less than primary or primary or more), length of stay in the nursing home (<3 or ≥3 years), dementia (yes or no), number of chronic conditions other than dementia (0–2 or ≥3), and functional dependency (no/mild, moderate, or severe/total).
