Figure 1. Addiction Vulnerability and Allostasis Models Conceptualized for Cannabis Users with Mental Illness.
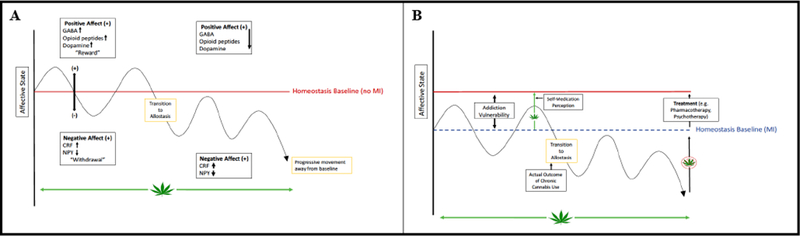
Individuals without mental illness (MI) (A) who use cannabis transition to an allostatic state, leading to neurobiological changes that induce a continuous reduction in positive affect that is associated with further use in attempts to regain original homeostatic levels. Individuals with MI (B) already have a lowered set point for positive and negative hedonic homeostasis, promoting addiction vulnerability, as substances are used in attempts to normalize an already altered (reduced) set point. Addiction in psychiatric patients is associated with a similar transition to an allostatic state but with an even lower homeostatic baseline (see dashed line in Panel B), with cannabis use continuing in attempts to regain the original positive affect experienced prior to substance use.
