Fig. 4.
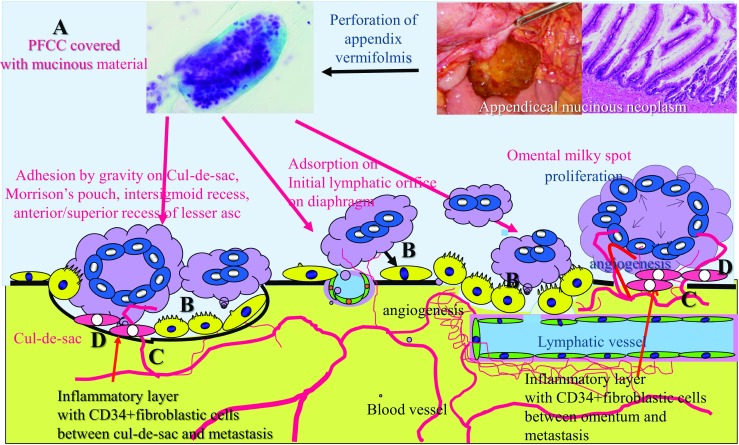
Superficial growing metastasis. Peritoneal free cancer cells (PFCCs) from the primary low-grade mucinous neoplasm are covered with mucinous material (A) and cannot invade the submesothelial tissue through the trans-mesothelial or trans-lymphatic routs because of their large size. PFCCs settle on the pelvic peritoneal surface by gravity, or adsorbed to the omental milky spots or diaphragmatic stomata (B). Then PFCCs proliferate on the peritoneal surface aided by neovascularization with subperitoneal blood capillaries (C) induced by CD34-positive interstitial cells between peritoneum (D, as shown in orange)
