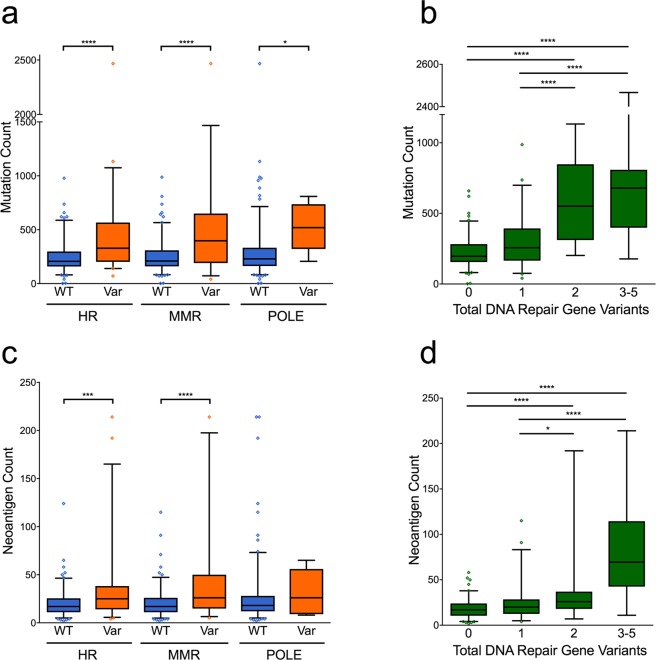
Figure 1.
DNA repair gene variants are associated with increased mutation and neoantigen count. (a) Presence of somatic variants in homologous recombination (HR), mismatch repair (MMR) or polymerase epsilon (POLE) were associated with increased mutation burden. (b) Mutation count increases with higher number of DNA repair gene variants. (c) Neoantigen burden similarly was associated with DNA repair gene variants and (d) with the number of affected genes. Statistical analysis completed with Student’s t-test (a,c) and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons (b,d), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.