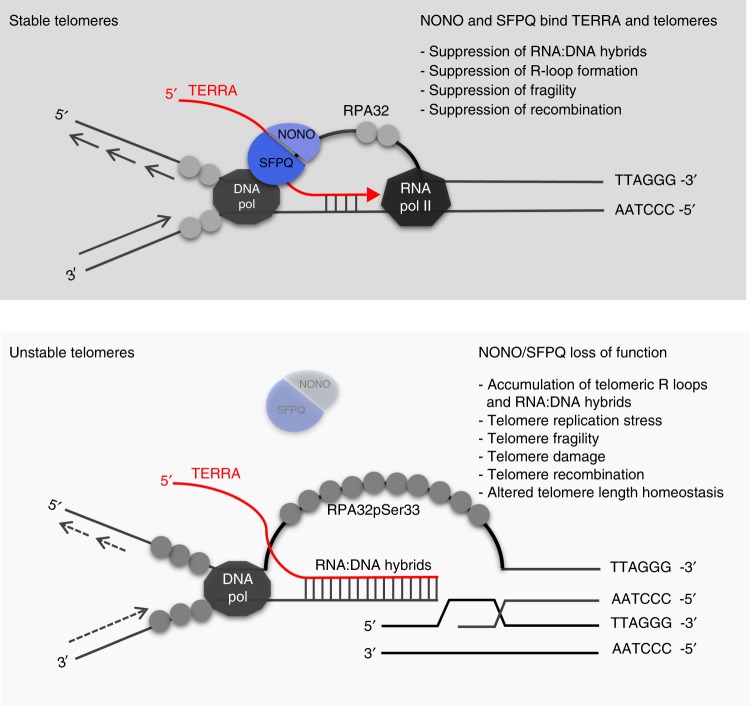
Fig. 7.
A model for the role of NONO and SFPQ in controlling telomere stability. Top panel: NONO and SFPQ bind TERRA transcripts at telomeres and control mechanisms that antagonize the accumulation of RNA:DNA hybrids, thereby stabilizing telomeres. Bottom panel: Loss of NONO and SFPQ leads to the accumulation of RNA:DNA hybrids at telomeres, resulting in the displacement of the non-template telomere strand (G-strand) and R-loop formation. Increased R-loop formation triggers replication defects, fragility, telomere damage and the exposition of recombinogenic telomeric DNA that engage in telomere recombination events and result alterations in telomere length homeostasis. DNA pol, DNA polymerase; RNA pol II, RNA polymerase II