Figure 2.
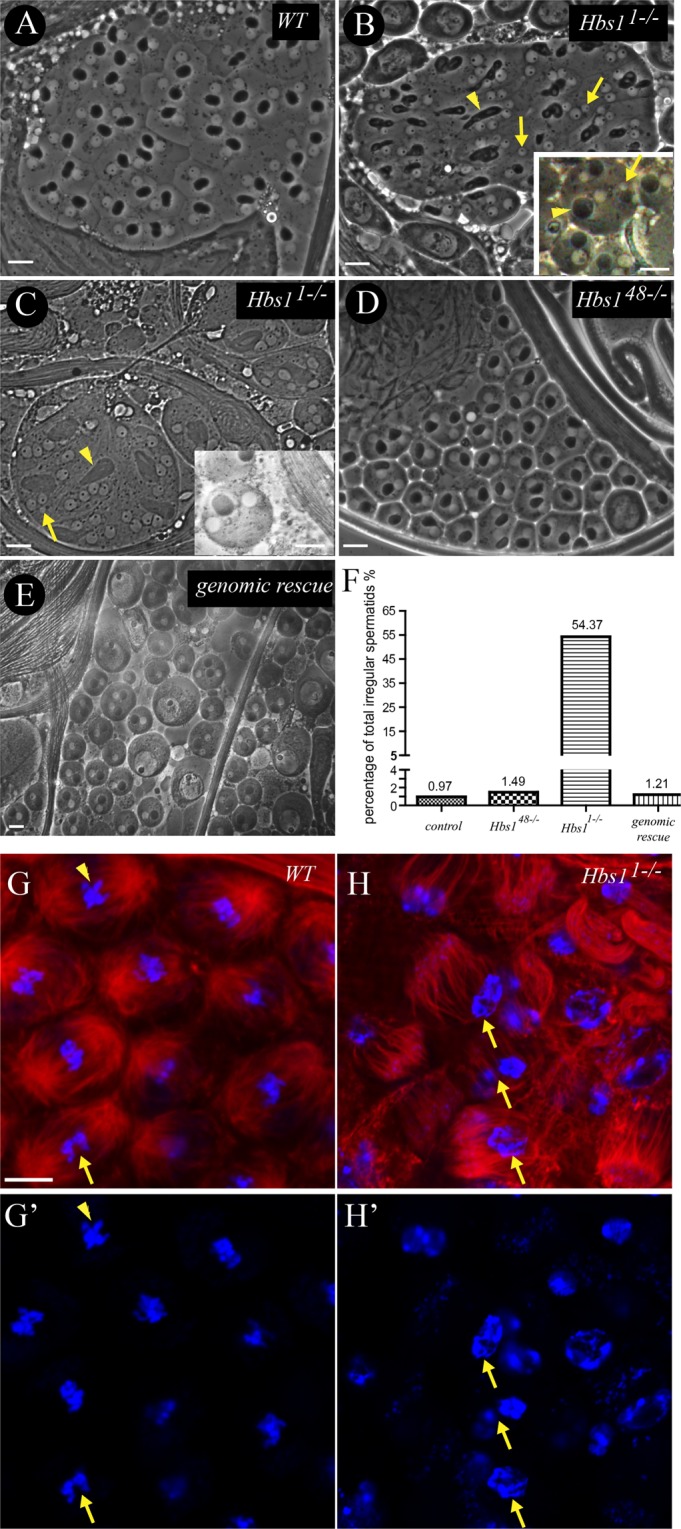
Hbs1 is required for male meiosis. (A) In wild-type cysts, each spermatid contained one nebenkern (dark) to one nucleus (light) (1:1 in ratio) of similar sizes. (B,C) In some of the Hbs11−/− mutant cysts, heterogeneous mixture of ratios of nebenkern to nucleus (from 1:1, 1:2, 1:3 to 1:4) and abnormal large nebenkern(arrow heads) with small or micronuclei(arrows) were frequently observed, which was evidence of failure of cytokinesis and chromosome mis-segregation (See Table 1 for the quantitative data). (D) The meiotic figure appeared normal in Hbs148−/− mutant cysts. (E) Normal onion stage spermatids were observed in the Hbs1 genomic rescued testis. (F) There was greater percentage of total irregular spermatids in the Hbs11−/− testes. (G,H) The wildtype testis (G–G’) exhibited fully formed and well-focused spindle poles, and the condensed chromosomes were either at the metaphase plate (arrowhead) or beginning to separate (arrow). In Hbs11−/− testes, the spindle microtubules failed to converge into the poles and were splayed outward, and the chromosome could not be correctly separated (arrow).α-tubulin staining is in red, and DAPI is in blue. Scale bars = 10 μm.
