Fig. 4.
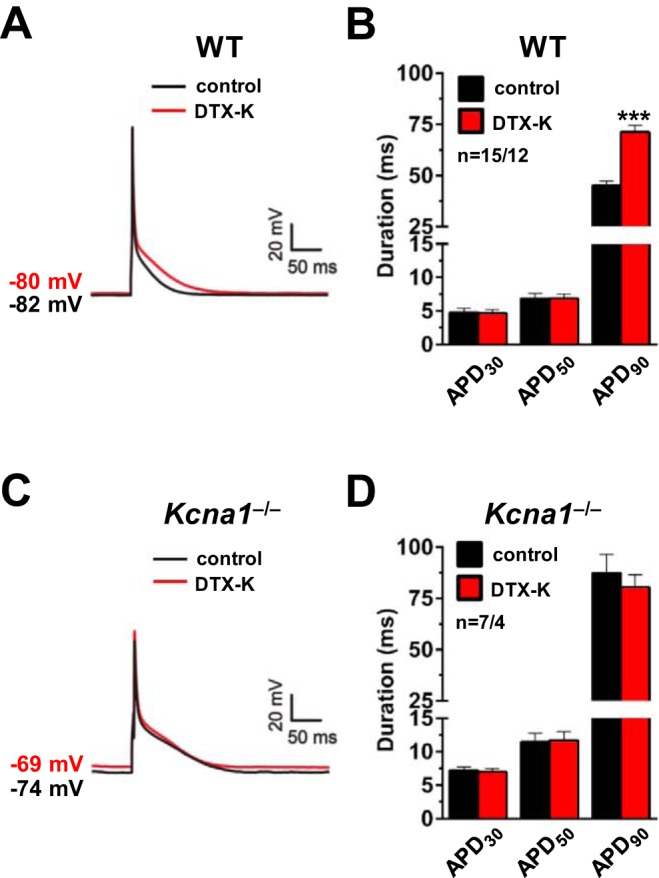
Dendrotoxin-K (DTX-K) prolongs action potentials in wild-type (WT) atrial myocytes. A: a representative action potential recording in a WT cell at baseline (black line; labeled control) overlaid with the resulting action potential after application of 10 nM DTX-K (red line; labeled DTX-K). B: average action potential duration (APD) in WT cells at 30, 50, and 90% repolarization (APD30, APD50, and APD90) before (control) and after (DTX-K) application of 10 nM DTX-K. C: a representative action potential recording in a Kcna1−/− cell at baseline (black line; labeled control) overlaid with the resulting action potential after application of 10 nM DTX-K (red line; labeled DTX-K). D: average APD in Kcna1−/− cells at APD30, APD50, and APD90 before (control) and after (DTX-K) application of 10 nM DTX-K. The resting membrane potential before and after DTX-K is indicated next to each waveform. Sample numbers (n) indicate myocytes per mouse. ***P ≤ 0.001 (2-tailed paired Student’s t-test).
