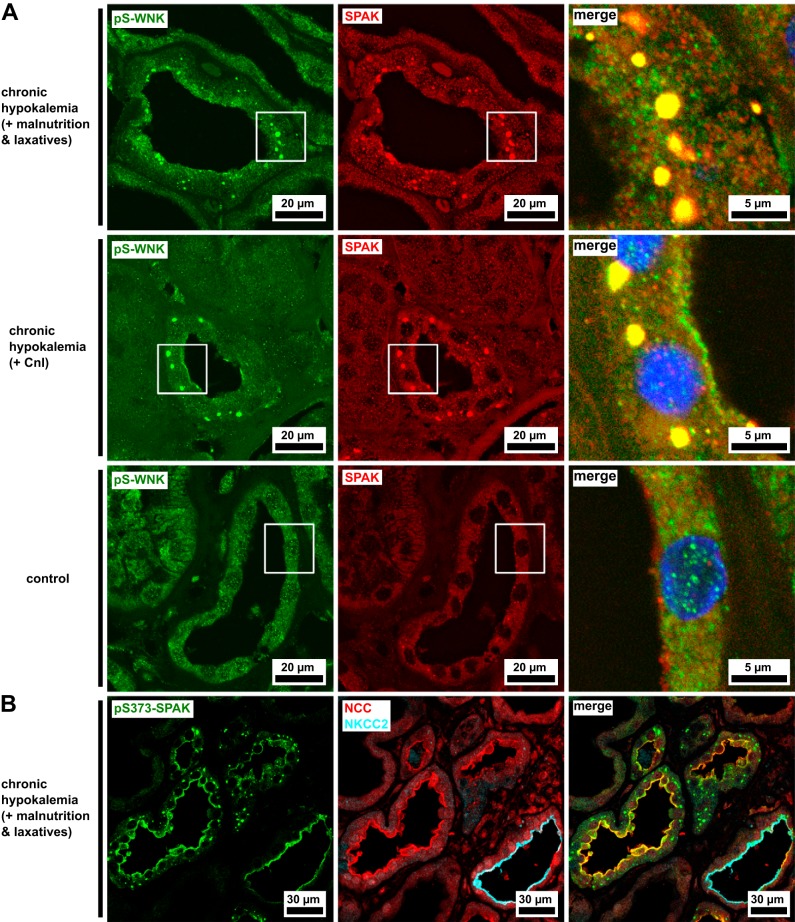
Fig. 1.
Punctate inclusions of Na+-Cl− cotransporter (NCC)-activating kinases in the cytoplasm of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) of patients with hypokalemia. A: the DCT is enriched with Ste20-related proline-alanine-rich kinase (SPAK) accumulations in both patients with hypokalemia but not in a morphologically normal control. The SPAK-positive structures in the patients with hypokalemia are also labeled by antibody against residues 375–389 of human with no lysine kinase-1 phosphorylated on Ser382 (pS-WNK). B: antibody against residues 367–379 of human SPAK phosphorylated on Ser373 (pS373-SPAK) is found in the luminal membranes of both the thick ascending limb [where it is colocalized with the type 2 Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter (NKCC2)] and the DCT (where it is colocalized with NCC). Its punctate cytoplasmic signal is limited to the DCT. Representative image of a patient with hypokalemia. Blue channels show DAPI nuclear counterstain. CnI, calcineurin inhibitors.