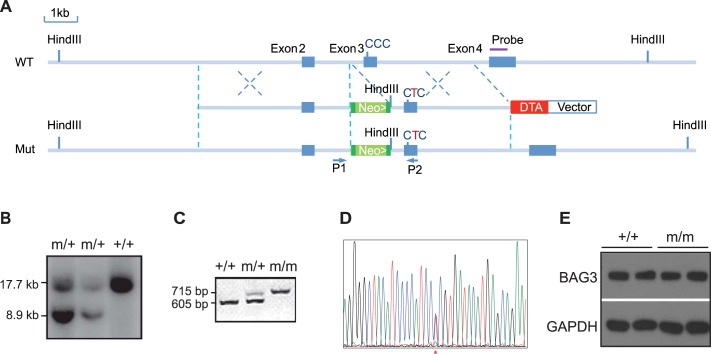
Fig. 1.
Generation of Bcl-2-associated athanogene 3 (Bag3) P209L knockin (KI) mice. A: targeting strategy. A restriction map of the relevant genomic region of Bag3 (top), targeting construct (middle), and mutated locus after recombination (bottom) is shown. Neo, neomycin resistance gene; DTA, diphtheria toxin A chain gene. Green boxes abutted to the Neo gene indicate flippase recognition target (FRT) sites. B: detection of wild-type (WT) (+) and mutant (m) alleles by Southern blot analysis with the probe diagrammatically represented in A after digestion with HindIII. C: genotyping of P209L KI mutant mice by PCR analysis of DNA isolated from tails using primers (P) diagrammatically represented in A. D: DNA sequencing confirmed insertion of the successful P215L mutation (equivalent to the human P209L mutation) from CCC to CTC (*). E: representative Western blot analysis of BAG3 in WT (+/+) and Bag3 P209L KI mutant (m/m) mouse hearts. GAPDH served as a loading control. n = 4 mice/group.