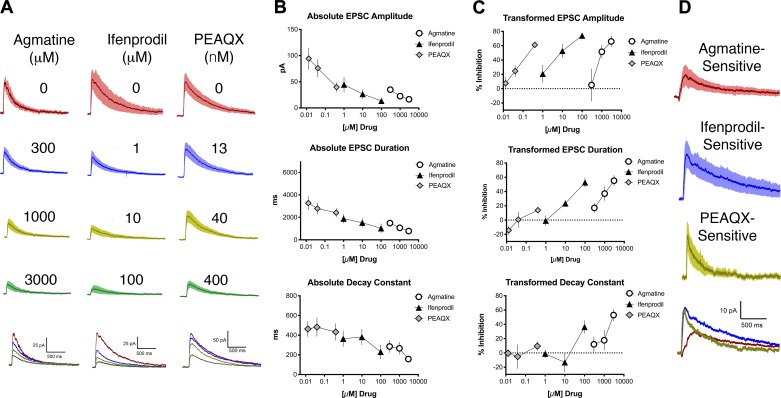
Fig. 2.
Agmatine decreases the amplitude, duration, and decay constant of blue light-evoked N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAr)-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) in a concentration-dependent manner. A: averaged blue light-evoked NMDAr-mediated EPSCs, with SE (shading), before (baseline, top traces for each drug) and after application of various concentrations of drug. For each set of traces, drug concentrations from top to bottom are as follows: agmatine 300, 1,000, and 3,000 µM; ifenprodil 1, 10, and 100 µM; PEAQX 13.3, 40, and 400 nM. Bottom traces show averaged EPSCs for all 3 concentrations with the baseline (no drug) represented for each treatment group by a red line, the lowest concentration for each drug by a blue line, the intermediate concentration by a yellow-green line, and the highest concentration by a green line. B: concentration-response relationships for absolute values of amplitude, duration, and decay constant of blue light-evoked NMDAr-mediated EPSCs for agmatine (circles), ifenprodil (triangles), and PEAQX (diamonds). C: transformed concentration-response relationships for amplitude, duration, and decay constant of blue light-evoked NMDAr-mediated EPSCs for agmatine (circles), ifenprodil (triangles), and PEAQX (diamonds) from the data shown in B. PEAQX did not decrease the evoked EPSC (eEPSC) decay constant, but it did decrease the eEPSC amplitude, suggesting antagonism of GluN2A-containing NMDArs. D: plots of EPSC difference currents (baseline trace minus highest drug concentration trace) for agmatine-, ifenprodil-, and PEAQX-sensitive components of NMDAr EPSCs based on the data shown in A, with agmatine represented by the red line, ifenprodil by the blue line, and PEAQX by the yellow-green line.