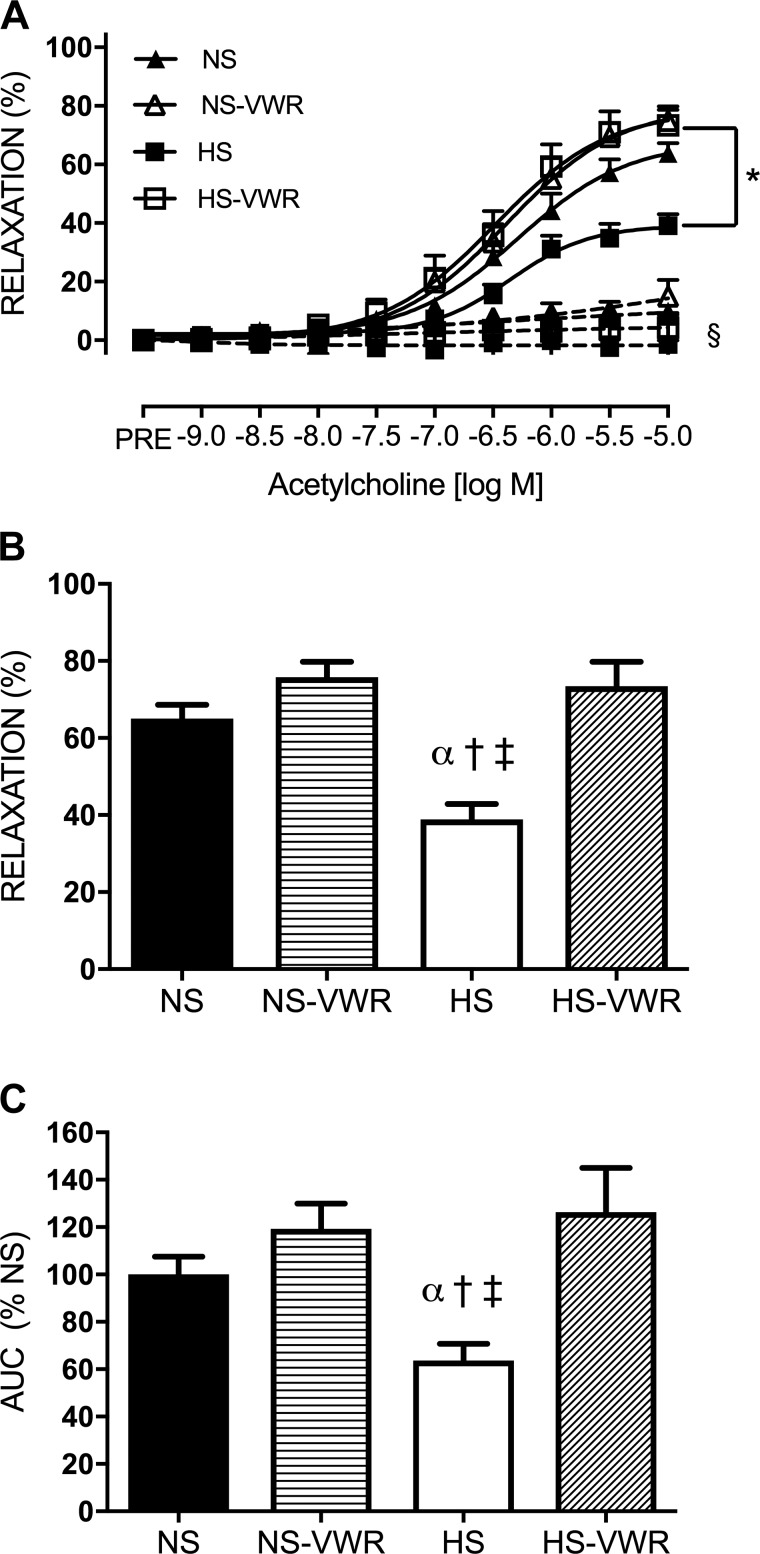
Fig. 1.
Endothelium-dependent relaxation (EDR) in sedentary and voluntary wheel running (VWR) rats fed either a normal-salt (NS) or a high-salt (HS) diet: dose responses of femoral rings to acetylcholine (ACh) under control (solid lines) and NG-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME)-treated (dashed lines) conditions (A), maximal relaxation (Emax) to ACh (B), and area under the curve (AUC) to ACh (C). Values are means ± SE; n: NS = 12, NS-VWR = 13, HS = 14, HS-VWR = 12. Data analysis was performed with a 1-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s post hoc test. *vs. HS, α vs. NS, †vs. NS-VWR, ‡vs. HS-VWR, §vs. respective control group (P < 0.05).