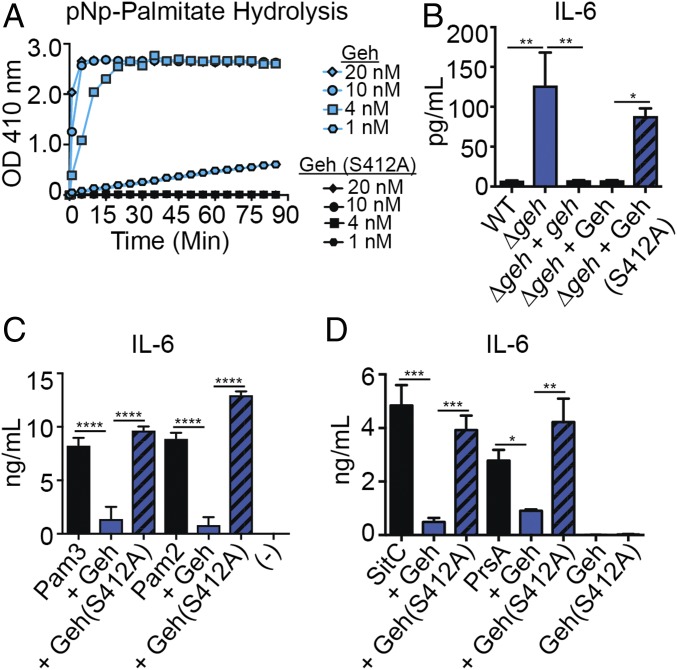
Fig. 6.
Ester hydrolase activity of Geh is required for lipoprotein inactivation. (A) pNp-palmitate hydrolysis (absorbance at 410 nm) in the presence of 1 nM, 4 nM, 10 nM, and 20 nM Geh(S412A). (B) IL-6 (pg/mL) production by BMMs after addition of cell-free supernatant from WT, Δgeh, and Δgeh + geh strains and from Δgeh supernatant supplemented with 10 nM Geh, Δgeh supernatant supplemented with 10 nM Geh(S412A), and Geh(S412A) alone (10 nM). (C) IL-6 (ng/mL) production by BMMs after addition of Pam2CSK4/Pam3CSK4 (10 ng/mL), Geh-treated Pam2CSK4/Pam3CSK4 (10 ng/mL), and Geh(S412A)-treated Pam2CSK4/Pam3CSK4 (10 ng/mL). (-), medium alone. (D) IL-6 (ng/mL) production by BMMs after addition of Pam3CSK4 (10 ng/mL), SitC/PrsA (100 ng/mL), Geh-treated SitC/PrsA (100 ng/mL), Geh(S412A)-treated SitC/PrsA (100 ng/mL), Geh (40 ng/mL), and Geh(S412A) (40 ng/mL). All experiments were repeated at least three times. Data shown in B–D are mean ± SD from three representative independent experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.