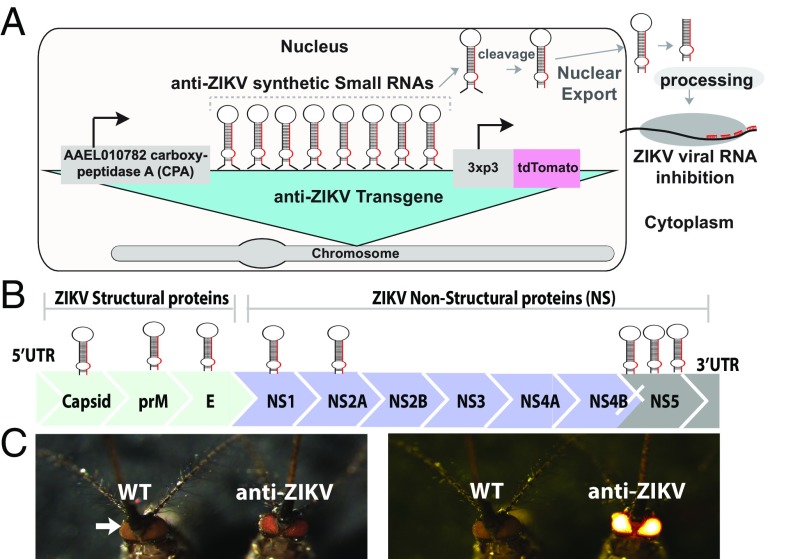
Fig. 1.
Schematic of anti-ZIKV transgene, ZIKV target sites, and phenotype of transgenic mosquitoes. (A) Schematic of the anti-ZIKV transgene used in the study, consisting of a CPA (AAEL010782) promoter driving expression of a polycistronic cluster of eight synthetic small RNAs engineered to target conserved genes in the ZIKV genome. Following processing, the small RNAs and their target ZIKV viral RNA interact in the cytoplasm. (B) Schematic of the ZIKV genome, consisting of three structural proteins [capsid, membrane precursor (prM), and envelope (E)] and seven nonstructural proteins (NS1, NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, and NS5), with relative synthetic small RNA targets indicated by hairpins above. (C) Higgs WT and TZIKV-C adult mosquitoes were imaged under both transmitted light and a fluorescent dsRED filter. Fluorescence is evident in mosquito eyes (indicated by white arrow).