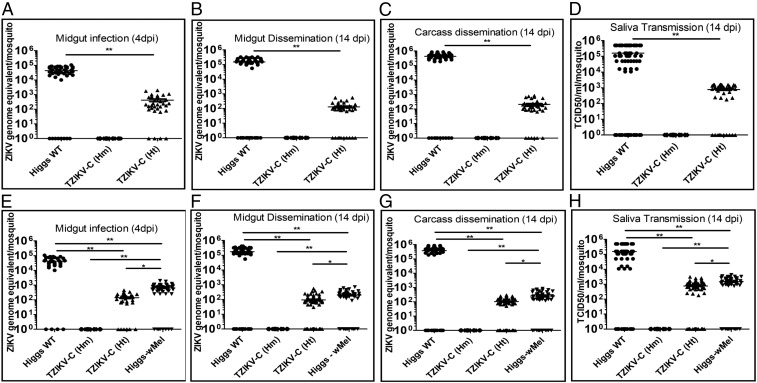
Fig. 2.
ZIKV replication and titers in Higgs WT, TZIKV-C, and Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes challenged with either a Cambodian or Puerto Rican ZIKV strain. ZIKV genome copies and titers in Higgs WT, TZIKV-C homozygous (Hm) and heterozygous (Ht) transgenic, and Wolbachia-infected Higgs WT (Higgs-wMel) mosquitoes following a blood meal infected with a Cambodian (FSS13025, A–D) or Puerto Rican (PRVABC59, E–H) strain of ZIKV are shown. ZIKV genome-equivalents from mosquito midgut [4 dpi (A and E) and 14 dpi (B and F)] and carcass [14 dpi (C and G)] of Higgs WT and transgenic mosquitoes were determined using real-time RT-qPCR and calculated using previously published methods. (D and H) Virus titers in the saliva collected from Higgs WT and transgenic mosquitoes at 14 dpi were determined using a median tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50) on Vero cells and plotted. Higgs WT mosquitoes (●),TZIKV-C Hm transgenic mosquitoes (♦),TZIKV-C Ht mosquitoes (▲), and Higgs-wMel mosquitoes (▼) are shown. Horizontal bars represent the mean virus titer. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001. For each experiment, data from three replicates are pooled.