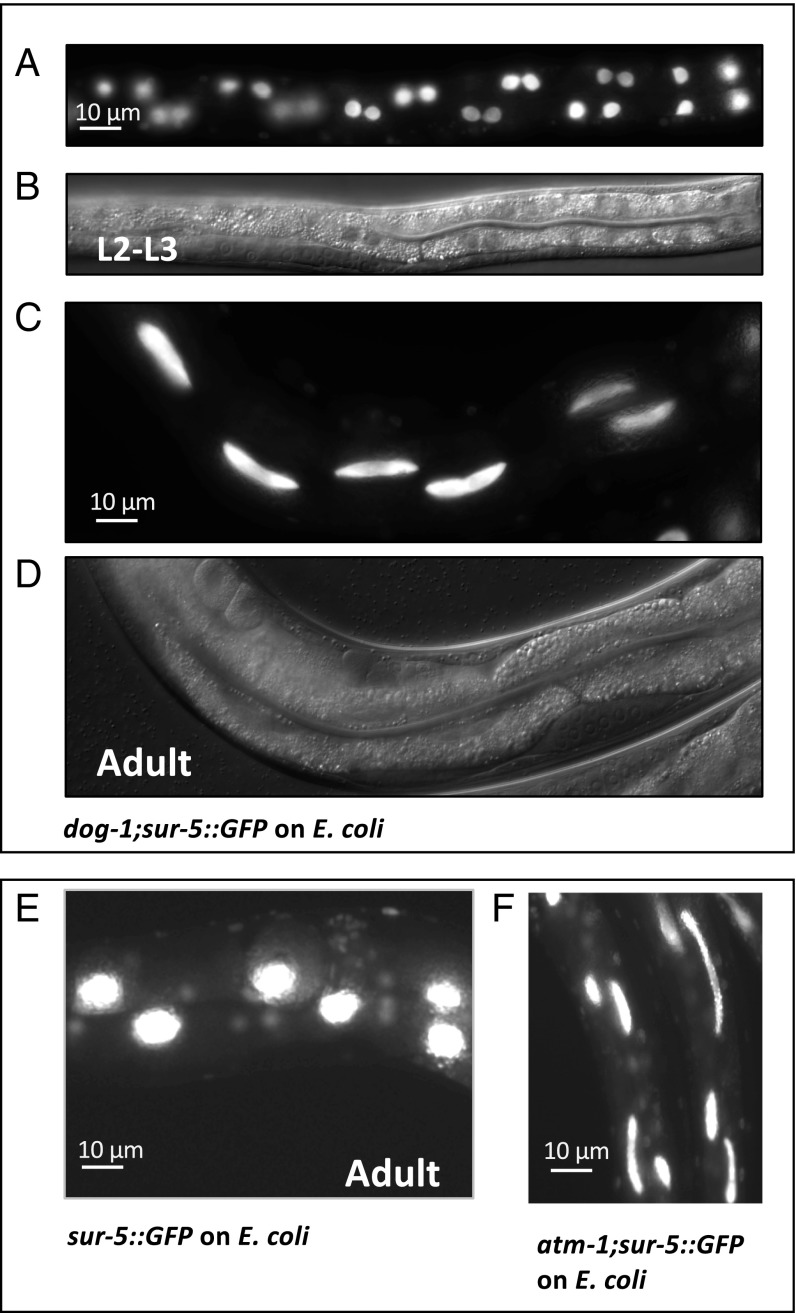
Fig. 3.
C. elegans strains with mutations in DNA damage response pathways grown on E. coli show the same defective nuclear division phenotype observed in WT C. elegans fed with Rhizobium huautlense. (A–D) Fluorescence and differential interference contrast sur-5::GFP images of C. elegans dog-1 mutant animals grown on E. coli illustrate failed intestinal nuclei segregation in L2-L3 larvae (A and B) resulting in “elongated” gut nuclei phenotype in adults (C and D). (E and F) Fluorescence images of gut nuclei patterning in sur-5::GFP (E) and the atm-1;sur-5::GFP adults (F) (one of the extreme cases). Intestinal karyokinesis is affected in 100% of atm-1;sur-5::GFP and dog-1;sur-5::GFP mutants fed with E. coli (SI Appendix, Table S1); other tissues were not evaluated.