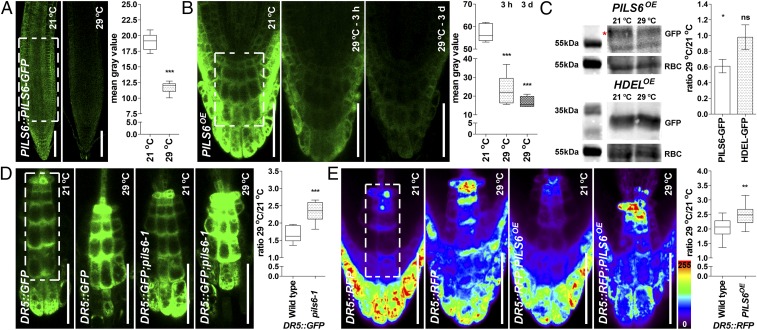
Fig. 3.
HT affects PILS6 protein level and PILS6-dependent auxin signaling. (A–C) HT down-regulates PILS6 protein level. Confocal images and quantification of PILS6-GFP fluorescence show that HT reduces the PILS6 protein levels in roots of PILS6::PILS6-GFP (A) and PILS6OE (B). Note that the response of PILS6 protein to HT is fast, showing dramatic reduction (about 60%) already after 3 h. Immunoblot with anti-GFP antibody and quantification of signal intensity (C) showing that HT down-regulates protein levels in PILS6OE seedlings, but not in 35S::HDEL-GFP (HDELOE) control line. RuBisCo (RBC) antibody was used for normalization. The red asterisk marks the PILS6-GFP, which runs above a nonspecific band. Please note that the 55kDa molecular weight marker for RBC is duplicated because the loading controls originated from the same protein immunoblot. The statistical evaluation shows the differences between the respective 21 °C and 29 °C values. (D and E) HT affects PILS6-dependent auxin signaling. Confocal images and quantification of DR5::GFP (D) or DR5::RFP (E), showing a relative increase in auxin response in roots of pils6-1 (D) and PILS6OE (E) when exposed to HT. The white dashed boxes represent defined ROIs in the most representative regions of the root, used to quantify the respective signal intensities. [Scale bars, 100 μm (A) and 50 μm (B, D, and E).] n = 7 (A), 6 (B), 9 (D), and 12 (E) roots. ns, not significant; *P = 0.01–0.05, **P = 0.001–0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t test (A and C–E) or one-way ANOVA (B).