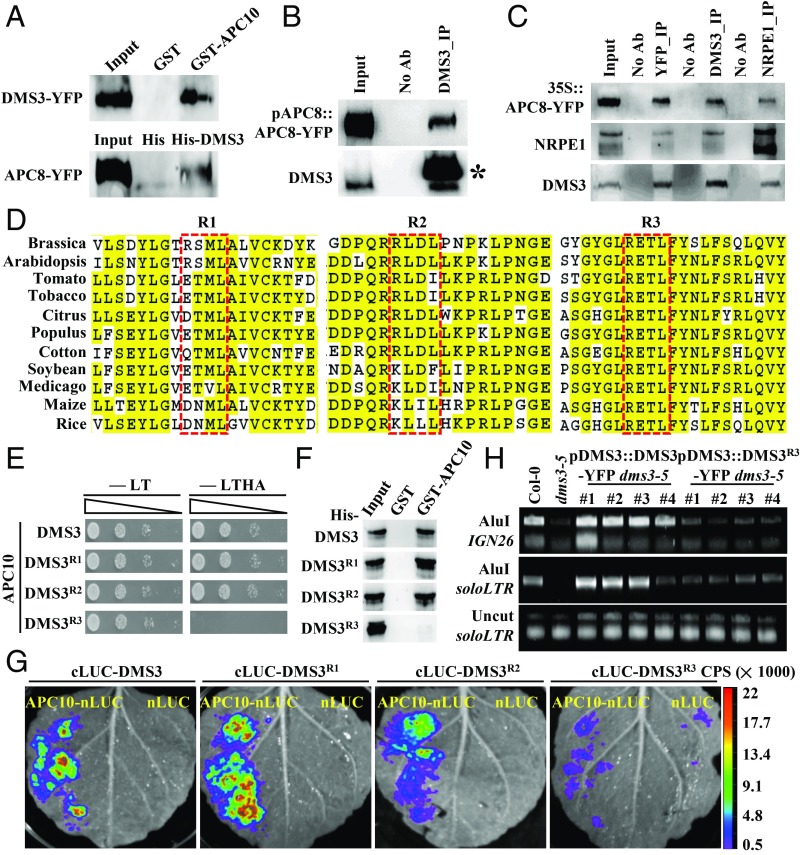
Fig. 3.
DMS3 interacts with APC10 in a D box-dependent manner. (A) Reciprocal semi-in vivo pull-down assays to examine the DMS3–APC/C interaction. (Top) GST-APC10 pulled down DMS3 from 35S::DMS3-YFP transgenic plants, and GST was used as the negative control. (Bottom) His-DMS3 pulled down APC8 from 35S::APC8-YFP transgenic plants, and His was used as the negative control. Precipitates were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-GFP antibodies. (B) Co-IP between APC8 and DMS3. Anti-DMS3 antibody coupled to the protein A beads was used to immunoprecipitate (IP) APC8 from inflorescence of pAPC8::APC8-YFP transgenic plants. Anti-GFP and anti-DMS3 antibodies were used to detect APC8 (Top) and DMS3 (Bottom) by Western blotting, respectively. The asterisk indicates the band of the heavy chain resulting from the excess anti-DMS3 antibody. (C) Reciprocal co-IP between APC8, NRPE1, and DMS3. GFP-Trap beads were used to immunoprecipitate DMS3 and NRPE1 from inflorescences of 35S::APC8-YFP transgenic plants. Alternatively, anti-DMS3– or anti-NRPE1–conjugated beads were used to immunoprecipitate other proteins from the same transgenic plants. Anti-NRPE1 (Middle), anti-DMS3 (Bottom), and anti-GFP (Top) antibodies were used to detect the corresponding proteins by Western blotting. (D) Alignment of the region flanking three D boxes of DMS3 from various species. DMS3 proteins from Brassica napus (XP_013693242.1), Gossypium hirsutum (cotton, XP_016737311.1), Arabidopsis thaliana (NP_566916.1), Medicago truncatula (XP_013461420.1), Glycine max (soybean, XP_006578904.1), Nicotina tobacum (tobacco, XP_016478774.1), Populus trichocarpa (XP_002321401.2), Citrus clementina (XP_006429697), Oryza sativa (Os01g13404.1), Solanum lycopersicum (tomato, Solyc06g051990.2.1), and Zea mays (maize, GRMZM2G309152_T01) were aligned using ClustalW. The red rectangles indicate the three D boxes. Identical residues are highlighted in yellow. (E) Y2H assays to test the interaction between APC10 and mutated DMS3. Yeast cells cotransformed by the indicated combinations of plasmids were diluted and spotted onto nonselective (-LT) and selective (-LTHA) media. (F) In vitro pull-down assays to examine the APC10–mDMS3 interaction. Protein precipitates were analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-His antibody. (G) Split luciferase complementation imaging assays to examine the interaction between APC10 and mutated DMS3. nLUC was used as a negative control. (H) Complementation assay to show the function of mutated DMS3 by Chop-PCR. DMS3 or DMS3R3 was introduced into dms3-5, and genomic DNA was digested by the DNA methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme AluI and subjected to semiquantitative PCR. The soloLTR locus was amplified using the undigested genomic DNA as the template for a control.