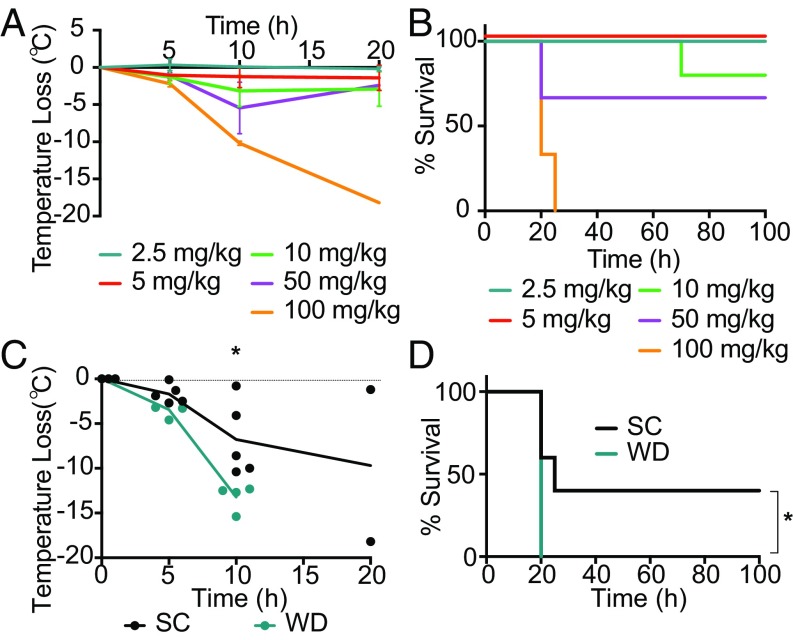
Fig. 4.
Increase in severity of sepsis in Western diet-fed mice is independent of the diet-associated microbiome. Age-matched male germ-free C57B/6 mice were injected i.p. with 2.5, 5, 10, 50, or 100 mg/kg of LPS and monitored for (A) temperature loss as a measure of disease severity and (B) survival. Age-matched male germ-free C57B/6 mice were fed SC or WD for 16 d and then injected i.p. with 50 mg/kg of LPS and monitored for (C) temperature loss and (D) survival. n = 3–5 mice/group in each independent experiment. For C, a Mann–Whitney U test was used for pairwise comparisons. For D, a log-rank test was used. For all panels, P values less than 0.05 were considered significant (*P < 0.05).