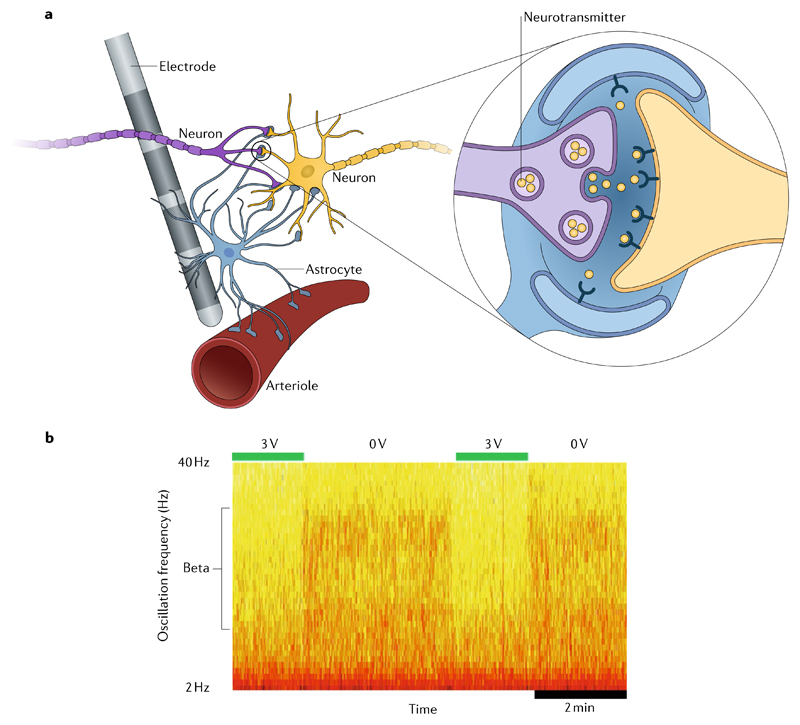
Fig. 1. Deep brain stimulation mechanisms.
a | Neurotransmitters (inset) are released in response to stimulation, leading to calcium waves and subsequent release of gliotransmitters. This release influences synaptic plasticity, leading to arteriole dilation and increased regional blood flow. b | Deep brain stimulation (DBS)-induced changes in local field potentials within the subthalamic nucleus. Activity in the beta band is rapidly reduced with DBS at 3 V and then resumes with stimulation off.