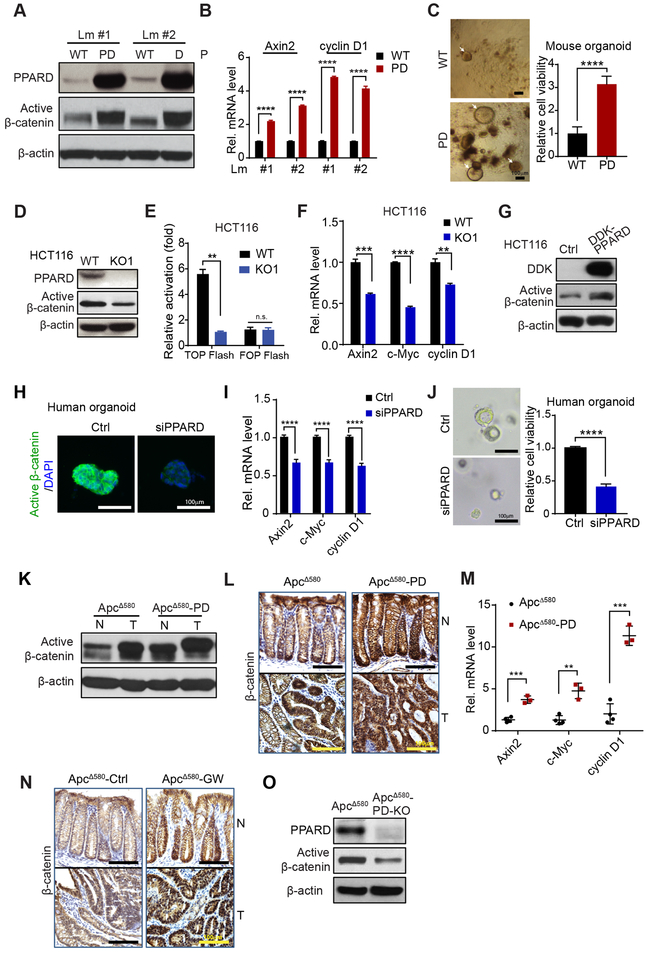
Figure 1.
PPARD activates β-catenin signaling in IECs. A and B, Active β-catenin protein levels (A) and mRNA levels of β-catenin target genes (Axin2 and cyclin D1) (B) in IECs of PD mice and WT littermates at age 10 weeks. Lm indicates littermate. C, The organoid-initiating capacity of IECs derived from PD mice and WT littermates at 6 weeks (n = 6 per group). Photomicrographs of primary organoids (left); and organoid cell viability measured by CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay (right). White arrows indicate individual organoids. D-F, Active β-catenin protein level (D), activity (E) and mRNA levels of Axin2, c-Myc, and cyclin D1 (F) in HCT116 cells without (WT) or with PPARD knockout (KO1). G, Active β-catenin protein levels of HCT116 cells stably transduced with control (Ctrl) or DDK-tagged PPARD (DDK-PPARD) lentiviral particles. H-J, Active β-catenin protein expression (H), mRNA levels of Axin2, c-Myc, and cyclin D1 (I), and representative organoid images and organoid cell viability (J) in human organoid cells transfected with control siRNA (Ctrl) or PPARD siRNA (siPPARD) for 48 hours (H and I) or 96 hours (J) (n = 3). K-M, Active β-catenin protein expression in normal and tumor IECs by Western blot (K); expression and localization of β-catenin in colonic normal and tumor tissues IHC (L); and Axin2, c-Myc, and cyclin D1 mRNA expression levels in normal IECs (M) of ApcΔ580 and ApcΔ580-PD mice at age 14 weeks. N, ApcΔ580 mice were fed a diet containing the PPARD agonist GW501516 (50 mg/kg) (GW) or a control diet (Ctrl) for 10 weeks, then evaluated for β-catenin expression by IHC. O, Active β-catenin protein expression in IECs of ApcΔ580 and ApcΔ580-PD-KO mice at age 14 weeks. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.