Figure 2 -.
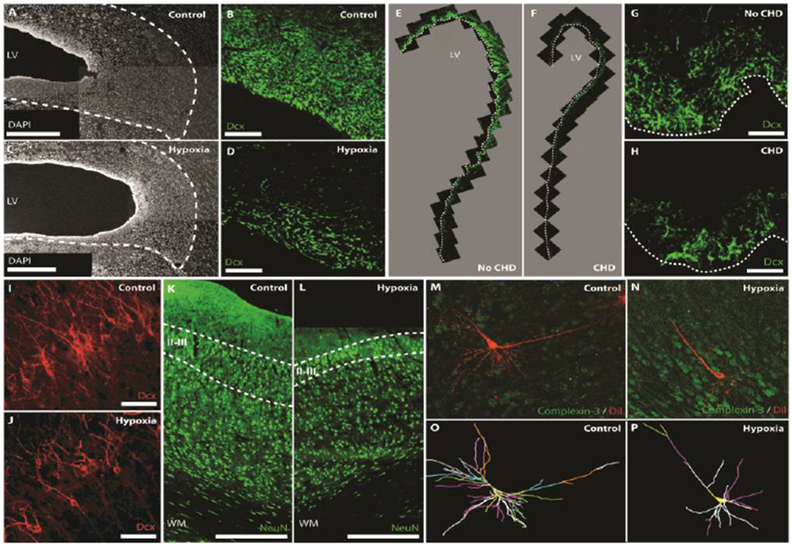
Cellular impairments in the perinatal brain associated with hypoxia and CHD.
Postnatal hypoxia in the piglet reduces the width of the SVZ (A,C; Scale bars, 500 mm) and the number of neuroblasts (DCX+) in the SVZ (B,D; Scale bars, 50 mm). Similarly, CHD reduces neuroblast numbers (DCX+) in the SVZ of human infants (E-H; Scale bars, 50 mm). Postnatal hypoxia in the piglet also reduces the number of DCX+ immature neurons (I,J; Scale bars, 50 mm) and NeuN+ mature neurons (K,L; Scale bars, 500 mm) in layers II/III of the frontal cortex. Prenatal hypoxia in the sheep results in a decrease in dendritic arborization of subplate neurons. 3D reconstructions of the soma and full basal and apical dendritic arbors (O,P) of representative sheep subplate neurons (M,N). Branch order rank is indicated by color: 1st order– bright yellow, 2nd order – white, 3rd order – purple/hot pink, 4th order – bright green, 5th order – cyan blue, 6th order – orange, 7th order – slate gray, 8th order – salmon pink, 9th order – forest green, and 10th order – bright blue. Adapted from Morton et al. [4] and McClendon et al. [75] with permission of the publishers.
