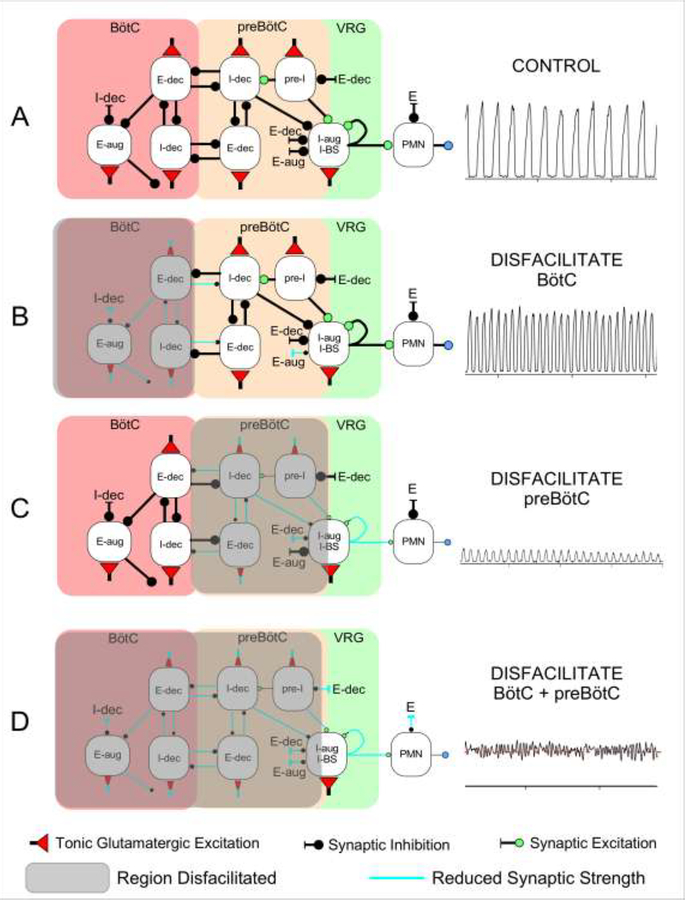
Figure 6:
Schematic of a hypothetical model for the effects of regional glutamatergic disfacilitation on the respiratory pattern. A: Control network configuration, B: Disfacilitation of the Bötzinger Complex (BötC), C: Disfacilitation of the preBötzinger Complex (preBötC), and D: Disfacilitation of both regions. Depicted are the inspiratory (I) and expiratory (E) neuronal discharge types located in the respective region, which are believed to underlie the mechanism of reciprocal inhibition. Color of the buttons indicates the type of synaptic connection with red: tonic glutamatergic excitation, green: (phasic) glutamatergic excitation, black: synaptic inhibition. aug: augmenting; dec: decrementing; VRG: ventral respiratory group; PMN: phrenic motoneuron; BS: bulbospinal neuron. Shaded region: disfacilitated neurons with reduced synaptic transmission. See Discussion for details.