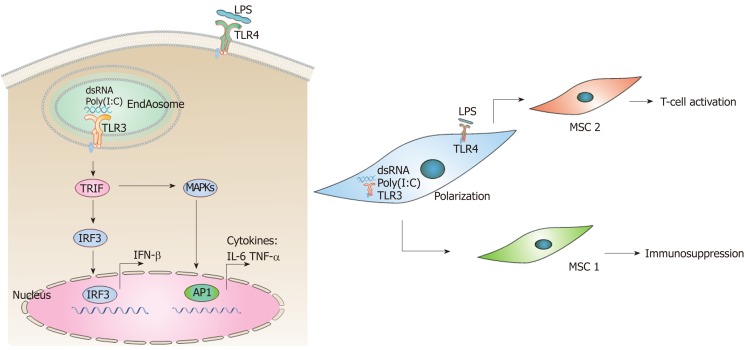
Figure 2.
Poly(I:C)-toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway and polarization of mesenchymal stem cells. A: Poly(I:C)-induced toll-like receptor 3(TLR3) signaling pathway. TLR3 recognizes dsRNA analog poly(I:C) in the endosomes and initiates signaling by TRIF, leading to activation of IRF3 and induction of IFN-β. TRIF-dependent signaling pathway also induces activation of MAPKs and AP-1, and culminates in the production of inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and TNF-α; B: Polarization of MSCs into MSC1 (M1 type with a proinflammatory response) and MSC2 cells (M2 type with an anti-inflammatory response) as a result of activation of TLR3 and TLR4 respectively. Poly(I:C): polyinosinic–polycytidylic acid; dsRNA: Double-stranded RNA; TLR3: Toll-like receptor 3; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; TRIF: Toll–IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-β; IRF3: Interferon regulatory factor 3; MAPKs: Mitogen-activated protein kinases; AP1: Activator protein 1; IFN-β: Interferon β; IL-6: Interleukin 6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.